- Home
- Products
- Services
- Resources
- About Us
- News
- Contact

Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-07 Origin: Site
You may hear your doctor say HRD positive or HRD negative when talking about cancer. HRD positive means your cells cannot fix DNA damage well. HRD negative means your cells fix DNA damage easily. About half of patients are in each group:

Knowing your HRD status helps doctors choose your treatment. It can change which therapies work best for you.
HRD positive means your cells have trouble fixing DNA damage. This helps doctors pick the best treatments for you.
If you are HRD positive, some therapies may help more. PARP inhibitors and platinum-based chemotherapy can work better for you.
HRD testing gives important facts that help your cancer treatment plan. It can also make your results better.
You might wonder what HRD means. HRD stands for homologous recombination deficiency. This happens when your cells cannot fix certain types of DNA damage. Usually, your body has special tools to repair double-stranded breaks in DNA. When these tools do not work, mistakes build up in your DNA. These mistakes are called "scars." HRD often comes from changes in important genes, like BRCA1 and BRCA2. These genes help fix DNA. If they do not work, your cells cannot repair damage well.
Here is a quick look at the key features that define HRD:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations | Changes in these genes are strong signs of HRD. |
Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) | This means your DNA loses some of its variety, which can signal HRD. |
DNA repair mechanisms | Problems in these pathways lead to HRD and more DNA errors. |
HRD plays a big role in cancer. When your cells cannot fix DNA, they can turn into cancer cells more easily. Some cancers have HRD more often than others. For example, ovarian and breast cancers show higher rates of HRD. Prostate and pancreatic cancers can also have HRD, but not as often.
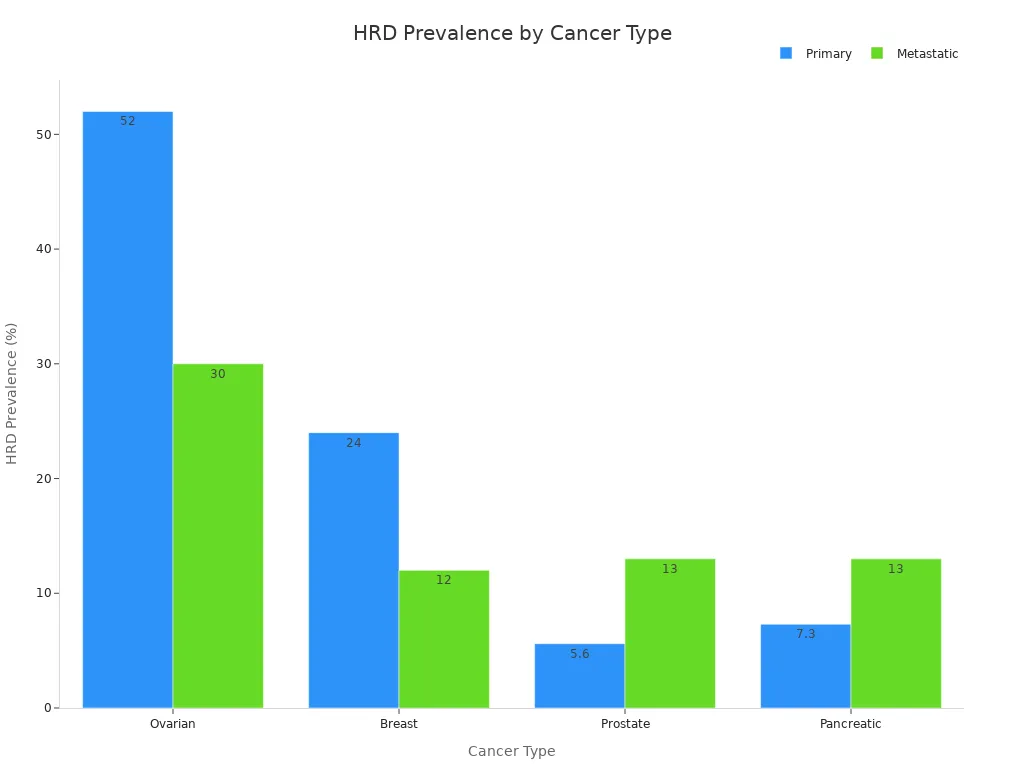
Knowing if your cancer has HRD helps your doctor choose the best treatment for you.
Doctors use special tests to see if you are HRD positive. These tests look for signs your cells cannot fix DNA damage. They check for changes in certain genes and patterns in your DNA. Here is a table that shows what doctors look for:
Criteria/Method | Description |
|---|---|
Pathogenic mutations in HRR genes | Mutations in genes like BRCA1 or BRCA2 show HRD positivity. |
Genomic instability measures | Loss of heterozygosity (LOH), telomeric allelic imbalance (TAI), and large-scale state transitions (LST) help spot HRD. |
Genomic scars | Special tests find DNA "scars" that mean your cells cannot repair damage. |
You do not need a BRCA mutation to be HRD positive. About 35% of HRD-positive tumors do not have a BRCA mutation. Doctors use a score called composite HRD score. This score combines LOH, TAI, and LST. If your HRD score is 50 or higher, or you have a BRCA mutation, you are HRD positive.
Some common tests for HRD are:
Myriad myChoice assay
Foundation Focus CDx BRCA LOH assay
Leuven HRD test
These tests help doctors find HRD-positive tumors in many cancers. Testing for HRD is important. It helps more patients get the right therapy.
If you are HRD positive, your treatment plan may change. Doctors know HRD-positive tumors respond better to some therapies. You may get more benefit from platinum-based chemotherapy or PARP inhibitors. These treatments work well because HRD-positive cells cannot fix the damage these drugs cause.
Let's see how HRD positivity affects your outlook and options:
Evidence Type | Findings | Implications |
|---|---|---|
Prognosis | High HRD score links to better outcomes in early TNBC patients | You may have a better prognosis |
Treatment Response | HRD-positive tumors respond better to platinum chemotherapy | You could benefit more from these treatments |
Immune Response | More immune cells attack HRD-positive tumors | This may help improve your survival rates |
Treatment Efficacy | Carboplatin doubles response rate in BRCA mutated patients | Carboplatin may be very effective for you |
Pathological Response | Adding carboplatin boosts pCR rate in TNBC | You may see better results with certain regimens |
Doctors also look at how long you stay cancer-free after treatment. In one study, HRD-positive patients stayed cancer-free for 9.4 months. HRD-negative patients stayed cancer-free for only 4.1 months. If you have a BRCA mutation, you may stay cancer-free even longer.
Tip: If your doctor says you are HRD positive, ask about PARP inhibitors and platinum-based chemotherapy. These options may give you the best chance for success.
HRD testing gives you and your doctor more information. It helps you get the treatment that works best for your cancer.
You may wonder how doctors know if you are HRD negative. They use special lab and genetic tests. These tests look for signs your cells fix DNA damage well. Doctors check for changes in your genes and other clues. If your cells repair DNA easily, you are HRD negative.
Here is a table showing some tests used for HRD testing and how they confirm HRD-negative tumors:
Test Name | Description | HRD Negative Status Confirmation |
|---|---|---|
BRACAnalysis CDx® | Finds germline BRCA1/2 mutations; does not confirm HRD status. | Only finds germline mutations, not somatic ones. |
FoundationOne® CDx | Finds mutations, gLOH, and other features; confirms HRD status. | HRD if BRCA is mutated or gLOH is 16% or more. |
TruSight™ Oncology 500 | Checks 523 genes; looks at HRD-LOH, LST, and TAI. | Matches other tests for HRD status. |
Liquid Biopsy (ctDNA) | Not very invasive; checks tumor differences. | Can give false negatives or positives. |
Doctors look at your test results to decide if your tumor is HRD negative. If your genes do not show HRD signs, you are in this group. Your doctor may say your tumor is HR-proficient. This means your cells fix DNA damage easily.
If you have HRD-negative tumors, your cells fix DNA damage better than HRD-positive ones. This can change your treatment choices. You may not respond as well to drugs that target DNA repair problems. But you still have options.
Let's look at what HRD-negative status means for you:
HRD status helps your doctor pick the best therapy.
HRD-negative tumors do not get as much help from PARP inhibitors as HRD-positive ones.
You can still get PARP inhibitors, but they may not work as well.
HRD-negative patients may need other treatments for the best results.
Here is what studies found about PARP inhibitors and HRD-negative tumors:
PARP inhibitors helped all ovarian cancer patients, no matter their HRD status.
HRD-positive patients got more help from PARP inhibitors.
HRD-negative patients got some help, but it was less.
Note: If your doctor says you have HRD-negative tumors, ask about all your treatment choices. You may still get PARP inhibitors, but your doctor may suggest other therapies too.
HRD testing gives you and your doctor important information. It helps you learn about your cancer and guides your choices. You can feel sure that doctors use the newest tests to find the best plan for you.
Labs use different tests to find your HRD status. Some tests look for changes in your genes. Other tests check for DNA "scars." These scars show your cells have trouble fixing themselves. Functional HRD assays, like the RECAP test, measure how well your tumor cells fix DNA right now. These tests help doctors guess how you might react to treatment.
Here's a quick look at how some HRD assays compare:
Assay | Sensitivity | Specificity | Clinical Utility Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ShallowHRD | 80% | 85.7-100% | Useful for research and VUS classification. |
HRDetect | N/A | N/A | Gives a deeper look at HRD signatures. |
Functional HRD assays show what is happening now. Genomic scar-based assays show old DNA repair problems. Labs use the CB-Gene HRD Reference Standard to check their HRD assays. This tool helps labs make sure their tests work well. It helps labs improve accuracy for patients.
Your HRD test report gives you more than a score. It tells you about your cancer risk. It shows how your disease might change. It helps your doctor pick the best treatment for you. Functional HRD assays and other tests help your doctor choose the right therapy.
Tip: Ask your doctor how your HRD assay results change your treatment plan.
Labs must check their HRD assays before using them for treatment. This step helps patients get the best care. Sometimes, different tests give different results. Labs use standards to keep tests reliable.
Challenge Description | Details |
|---|---|
Variability of assays | Different HRD assays may give mixed results. |
Need for optimization | Labs must refine testing methods for better outcomes. |
If you have questions about your HRD status, talk to your doctor. Good HRD assays help you get the best therapy.
You want the best chance to beat cancer. Homologous recombination deficiency helps doctors pick your treatment. HRD testing helps make a plan just for you. If you are HRD-positive, you may do better with special therapies. These therapies attack weak spots in your cancer cells.
Clinical trials show HRD testing helps doctors match treatments to you. Patients with HRD-positive tumors often live longer. For example, in ovarian cancer, HRD-positive patients did not reach the median progression-free survival. HRD-negative patients had 7.0 months.
Study Focus | HRD Status | Median PFS (mPFS) | Hazard Ratio (HR) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
NSCLC | HRD (+) | Not reached | 0.14 (95% CI: 0.04–0.54) | 0.03 |
NSCLC | HRD (−) | 7.0 ms | - | - |
HRD testing can change your treatment options. If you are HRD-negative, you may need a different plan. Clinical trials found HRD-positive patients had 13.6 months median progression-free survival with platinum chemotherapy. They only had 2.0 months with platinum-free therapy. HRD-negative patients did not show much difference between these treatments.
HRD testing helps you get a plan made for you.
Doctors use biomarkers like HRD to pick treatments.
Clinical trials support HRD testing for better survival.
PARP inhibitors are a kind of targeted therapy. These drugs block poly (adp-ribose) polymerase inhibitors. Cancer cells use these to fix DNA damage. If you are HRD-positive, you may get PARP inhibitors. HRD testing helps doctors decide if PARP is right for you.
Clinical trials show HRD-positive patients with brca1/2 mutations do well with PARP inhibitors. The OlympiAD trial found patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer and germline brca1/2 mutations lived longer with PARP inhibitors. HRD testing helps find patients who benefit most.
Evidence Description | Conclusion |
|---|---|
Patients will be considered eligible for PARPi therapy if they are found to harbour a HRD positive status as determined by CDx. | HRD positive status is crucial for determining eligibility for PARP inhibitors. |
Homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) status remains the most robust predictive biomarker for PARP inhibitor (PARPi) response. | HRD status is a key predictive biomarker for PARP inhibitor therapy. |
You might wonder how much PARP inhibitors help. Clinical trials show HRD-positive patients treated with veliparib and chemotherapy had 31.9 months median progression-free survival. Those with placebo had 20.5 months.
Treatment Group | Median PFS (months) | P-value |
|---|---|---|
Veliparib + Chemotherapy | 23.5 | <.001 |
Placebo + Chemotherapy | 17.3 | N/A |
HRD-positive with Veliparib | 31.9 | <.001 |
HRD-positive with Placebo | 20.5 | N/A |
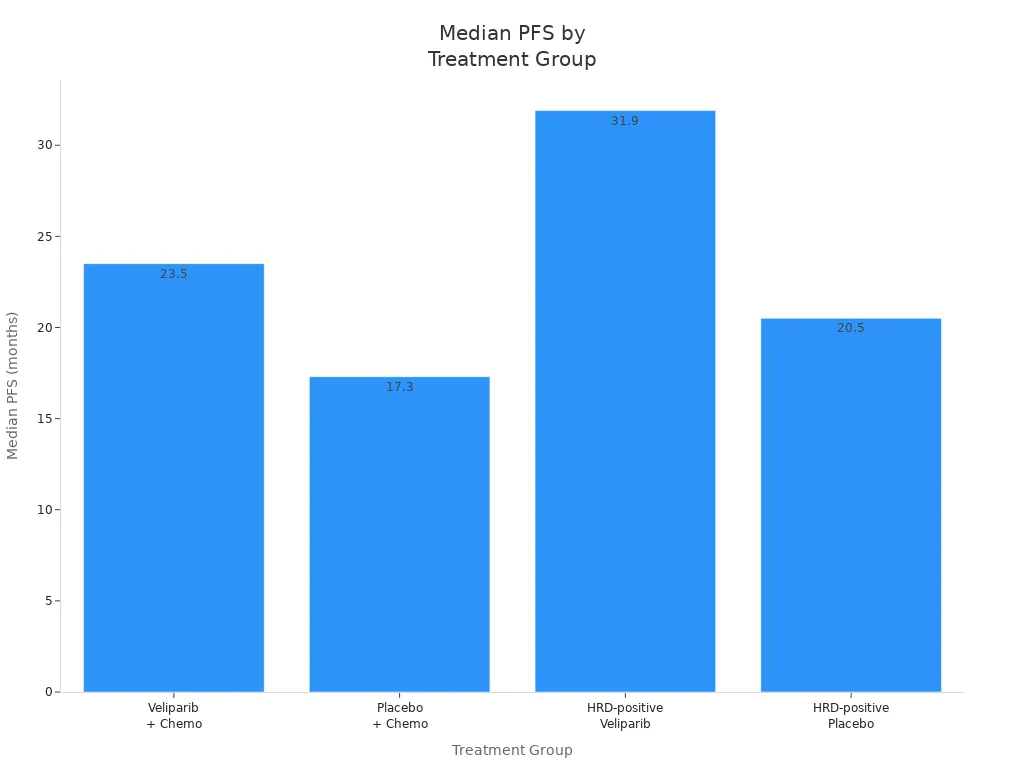
HRD testing helps you and your doctor pick the best therapies. You get a better chance to survive when your treatment matches your cancer's biomarkers.
You help decide your cancer treatment. Good HRD testing helps you and your doctor choose the right therapy.
About half of advanced ovarian cancers have HRD. Testing is important.
HRD-positive tumors work better with PARP inhibitors.
Treatment Option | HRD Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Niraparib Maintenance Therapy | HRD-positive | Helps patients who do well with platinum chemotherapy. |
Bevacizumab + Chemotherapy | HRD-negative | Used during chemo and for 12 months after as maintenance. |
You use HRD tests to find out if your cancer cells can fix DNA damage. These tests help your doctor choose the right clinical treatment for you.
Hrd tests give your doctor important clues. You get a better clinical plan because these tests show if you might respond well to certain clinical therapies.
You can trust HRD tests in most clinical settings. Labs use clinical standards to check HRD tests. Your clinical team uses these results to guide your clinical care.
Tip: Always ask your clinical team about your HRD tests. You want to know how these tests affect your clinical treatment plan.
This category is empty.