- Home
- Products
- Services
- Resources
- About Us
- News
- Contact

G6PD Reference Standard
Background
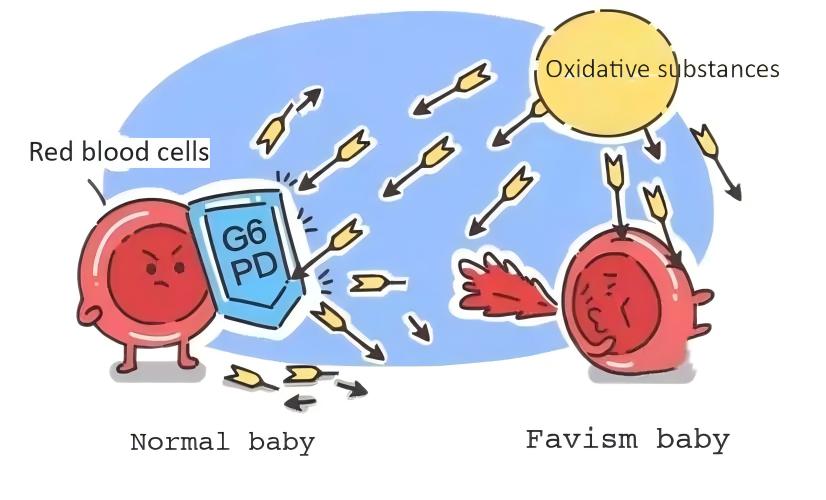
Favism, whose medical name is glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, is a genetic disease caused by mutation of the G6PD gene, which leads to reduced G6PD activity, and red blood cells cannot resist oxidative damage and are damaged, causing hemolytic anemia. Patients often develop the disease due to eating broad beans, commonly known as "favism", which is an X-linked incomplete dominant genetic disease. It is mostly caused by point mutations that change the spatial structure of the G6PD enzyme, thereby reducing enzyme activity. It is one of the most common red blood cell enzyme deficiency diseases.
Patients with G6PD deficiency cannot break down glucose normally. When exposed to oxidative substances such as broad beans, aspirin, and sulfonamides, they may experience acute hemolytic reactions, such as jaundice and poor spirits. In severe cases, they may experience rapid breathing, heart failure, and even shock. Neonatal G6PD deficiency is prone to hyperbilirubinemia and kernicterus, which can cause death or mental retardation, so prevention is the key to this disease. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the addition of information on the possible acute hemolysis of people with G6PD deficiency to the labels of chloroquine, dapsone, and rasburicase. Therefore, before using the above drugs, it is recommended to test for G6PD gene mutations, and patients with G6PD deficiency are prohibited from using the above drugs.
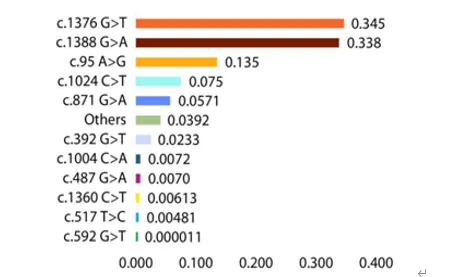
About 400 million people are affected worldwide, with an incidence rate of 15%-25%, mainly distributed in Africa, Latin America, the Mediterranean and Southeast Asia. In my country, the disease is characterized by high incidence in the south and low incidence in the north, with Hainan, Guangxi, Guangdong, Yunnan, Guizhou, Sichuan and other provinces as high-incidence areas, and less common in the north. With population mobility, areas with low incidence rates are also showing an increasing trend. Since my country started neonatal disease screening in 1981, many provinces and cities have gradually added screening items for G6PD deficiency. Common G6PD gene variants in my country include 95A>G, 392G>T, 487G>A, 493A>G, 592C>T, 1024C>T, 1360C>T, 1376G>T, 1388G>A, etc.
Detection Methods
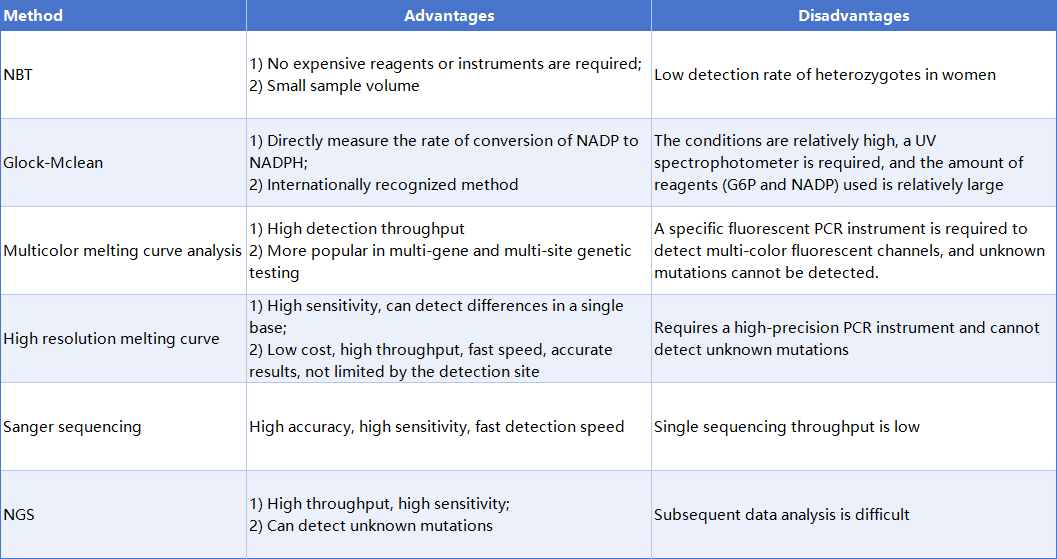
In the "Expert Consensus on Laboratory Testing Technology for Screening and Diagnosis of Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency in Newborns", when the neonatal disease screening for G6PD deficiency is positive, the enzyme level is confirmed using the G6PD/6GPD ratio method; multicolor melting curve analysis (MMCA) or direct DNA sequencing analysis is recommended for genetic diagnosis.
As of 2024, there are a total of 107 G6PD testing-related products, of which 4 are gene mutation detection kits.
Product Data
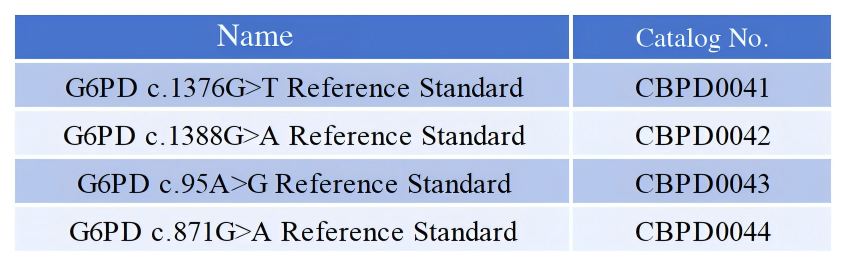
In the G6PD detection experiment, how to judge the accuracy of the results, standard products are indispensable. Kebai now launches G6PD-related standard products, mainly including female heterozygous standard products, and other sites will be launched in the future.
Some product data display
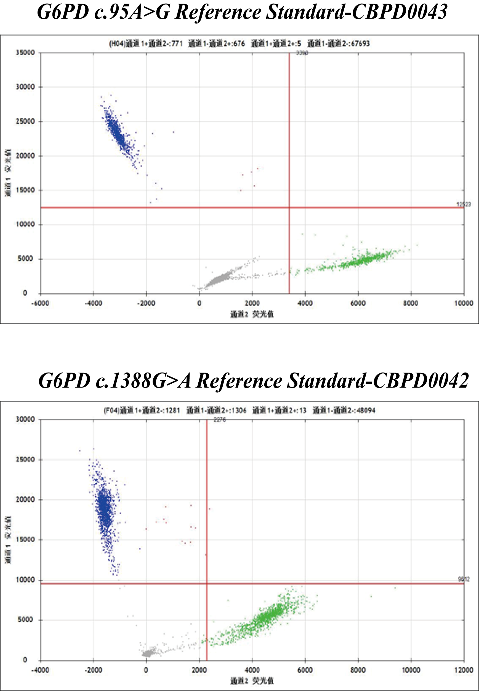
CB-Gene's G6PD standard uses Sanger sequencing to verify mutation sites, and uses ddPCR to accurately calibrate mutation frequencies. CB-Gene's G6PD gene mutation reference includes relatively common or high-incidence mutation types in clinical practice, which can help laboratories evaluate the performance of related products better and more effectively.
| Product Name | Catalog No. | Details | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|
| G6PD c.1376G>T Reference Standard | CBPD0041/42/43/44 | View detail » | Inquire |