- Home
- Products
- Services
- Resources
- About Us
- News
- Contact

Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-04 Origin: Site
You can use HRD testing to see if a tumor cannot fix DNA. This test helps doctors pick the best treatment for you. It is very useful for ovarian, breast, and prostate cancer. Many patients with non-BRCA1/2 gene changes show HRD positivity. Germline mutations often cause even higher rates. If you get a correct HRD result, you may have a better chance to use targeted therapies. Here are some important facts:
About 27.3% of people with non-BRCA1/2 gene changes test HRD positive.
Around 50% of advanced ovarian cancer cases show HRD.
Tumors with HRD respond well to PARP inhibitors, which help people get better results.
HRD testing finds tumors that cannot fix DNA. This helps doctors pick the best treatments.
About 27.3% of people with non-BRCA1/2 gene changes test HRD positive. This means they might get special treatments.
Tumors with HRD often work well with PARP inhibitors. This can help people with ovarian, breast, and prostate cancers.
Knowing your HRD status can help you and your doctor choose treatments. It can also help you get better results.
Always talk to your doctor about your HRD test results. This helps you understand what they mean for your treatment.
You may hear the term homologous recombination deficiency when learning about cancer. HRD means your tumour cannot repair DNA damage well. This problem happens when certain genes do not work as they should. Genes like BRCA1, BRCA2, RAD51C, and PALB2 help fix DNA breaks. If these genes stop working, your cells show genomic instability. This instability makes your tumour grow and change faster.
Here is a table showing some important genes and how they relate to HRD:
Gene | Role in HRD | How It Stops Working |
|---|---|---|
BRCA1 | Very important | Both copies can get damaged or lost |
BRCA2 | Very important | Both copies can get damaged or lost |
RAD51C | Important | Both copies can get deleted |
PALB2 | Important | Both copies can get deleted |
You can see that when these genes fail, your tumour may show HRD. HRD testing looks for these changes.
HRD acts as a key biomarker in cancer care. Biomarkers included in HRD testing help doctors know which treatments may work best for you. If your tumour has HRD biomarkers, you may respond better to certain drugs. For example, PARP inhibitors work well for tumours with HRD. Studies show that patients with high HRD scores often have better results. In lung cancer, a high HRD score links to longer survival and better response to immunotherapy. In triple-negative breast cancer, HRD helps doctors choose chemotherapy that works best.
Here is a table showing how HRD predicts treatment response:
Study | What It Shows |
|---|---|
NSCLC Immunotherapy | High HRD score means better survival and response |
NeoCART trial | HRD helps pick the right chemotherapy for patients |
You may wonder which cancers show HRD most often. HRD appears in many types, but some have higher rates. Ovarian cancer shows HRD in almost half of cases. Breast cancer and prostate cancer also show high HRD rates. Your tumour may have HRD even if you do not have a BRCA gene mutation.
Here is a table showing HRD rates in common cancers:
Cancer Type | HRD Prevalence Rate |
|---|---|
Ovarian | 47.7% |
Breast | 21.5% |
Prostate | 40.0% |
If your tumour has HRD, you may benefit from special treatments. HRD testing helps find these cases and guides your care.
You start HRD testing with a tumour tissue sample. Doctors get this sample during a biopsy or surgery. The sample goes to a lab for testing. Here is what happens next:
The lab takes DNA from the tumour tissue. Most tissue comes from special blocks called formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded blocks.
Technicians check the DNA using bright light methods. They look at how much DNA there is and if it is good quality.
The DNA is broken into pieces, cleaned, and copied. These steps help get the DNA ready for more tests.
Next-generation sequencing finds changes in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. The lab also checks for signs that the genome is unstable.
The lab puts together results from mutation tests and instability scores. This helps them figure out your HRD status.
You get a report that tells you your HRD status. Doctors use this report to help choose your treatment.
HRD testing helps you and your doctors know if your tumour cannot fix DNA. This can help you get better treatment choices.
Labs use different tools for HRD testing. Many labs use platforms like SeqOne's SomaHRD. This tool gives good results for ovarian cancer patients and does not cost too much. SOPHiA GENETICS works with Unilabs to test solid tumours using the SOPHiA DDM Platform. This platform uses smart computer programs to study next-generation sequencing data. The OncoScan platform uses a whole-genome microarray. It works with NGS panels to find BRCA mutations and other markers.
Labs have some problems when testing for HRD. Big parts of the genome can change in tricky ways. These changes make it hard to find copy number variations and can add extra noise. Labs use voting from many analysis methods to make results better. Using standard reference materials helps labs keep results correct and steady.
Here is a table showing how labs solve problems in HRD testing:
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
Reproducibility Challenges | Labs need strong agreement between alleles to keep results consistent. |
Complexity of HRD Regions | Large changes in the genome can cause false positives or negatives. |
Consensus Voting Approach | Using multiple analysis methods improves reliability. |
Standardized Reference Materials | Reference materials help labs keep results accurate and consistent. |
Reference standards help make sure HRD testing works well. Standards like CB-Gene's HRD Reference Standard are important for checking tests and lab quality. These standards act like real HRD-positive tumour samples. They have key genome features like pathogenic BRCA1/2 variants, loss of heterozygosity, telomeric allelic imbalance, and large state changes.
CB-Gene's HRD Reference Standard uses paired cell lines that live forever. These cell lines give a strong base for testing. The product has whole genome sequencing data and many HRD scores. This setup is like real sample conditions. You can use these standards to check your HRD tests and make sure your lab is high quality.
Tip: Reference standards help you see if your HRD testing works right. They help with skill testing and making new tests for cancer care.
Using reference standards makes HRD testing more trustworthy. This step helps doctors use HRD results to pick the best treatments for you.
When you get your HRD test results, you will see a score. This score shows how unstable your tumour’s DNA is. Doctors use these scores to help pick treatments for you. Labs may use different ways to measure HRD. This means your score can change from one test to another. Here are some things to remember:
Using the same scoring system helps doctors make good choices, especially for ovarian cancer.
Oncologists look at your HRD score, the type of test, and your whole medical history.
Reporting results in the same way helps doctors make better treatment decisions.
Note: Always ask your doctor to explain your hrd score. Ask how it fits with other test results and biomarkers.
You might wonder how HRD testing is different from other genetic tests. Some tests look for changes in just one gene. HRD testing checks for more changes linked to DNA instability. Tools like HRDetect use many mutational signs. They can find tumours with BRCA deficiency, even if there are no mutations. This makes hrd testing very useful for finding cancer biomarkers.
Here is a table showing how different tests work:
Test | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|
HRD Testing | 97% | 83% |
HRDetect | 99% | N/A |
ShallowHRD | 80% | 85.7% - 100% |
You can see that HRD testing and HRDetect both find most cases with DNA instability.
There are some limits to HRD testing. The test you choose and when you take it matter for good results. Not all negative results mean your tumour does not have DNA instability. Some people with low HRD scores may not get help from certain treatments. The quality of your tumour sample also affects your results.
Limitation/Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
Predictive Value | Negative HR test results do not always show the full story of HRD. |
Subgroup Analysis | Tumours with HRD scores below 33 may not respond well to platinum-based chemotherapy. |
Cutoff Score Variability | Different labs use different scoring systems, which can change how results are read. |
Tissue Quality | Poor quality tumour samples can make HRD testing less accurate. |
Tip: Make sure your tumour sample has enough tissue and is processed well. This helps you get the best hrd results and supports better cancer care.
Knowing your HRD status helps you choose your treatment. Tumour testing for HRD shows if your tumour cannot fix DNA. This makes your tumour easier to treat with some drugs. Platinum-based drugs and PARP inhibitors work well for HRD tumours. These drugs use synthetic lethality. They attack cancer cells that cannot repair DNA. The cells die because they cannot fix the damage.
Doctors use HRD as a biomarker to help pick treatments. This is important for ovarian, breast, and prostate cancers. If your tumour has HRD, you may get more help from these drugs. This is true for high grade serous ovarian cancer. It also helps in advanced high grade serous ovarian cancers. Knowing your HRD status helps you and your doctor make a good plan.
Here is a table that shows how guidelines use HRD and other biomarkers to help choose therapy:
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
HRD Testing | Used to help pick therapy in ovarian cancer, especially for PARP inhibitors. |
BRCA Testing | Used to check family risk and see if you can get PARP inhibitors. |
Additional Genes | Guidelines say to test other homologous recombination genes in ovarian cancer patients. |
Clinical Outcomes | HRD gene mutations can show how well you will respond to PARP inhibitors. |
Tip: Ask your doctor about HRD testing. It can help you find the best treatment for your cancer.
PARP inhibitors are targeted therapies that work well for HRD tumours. These drugs block the PARP protein. PARP helps fix DNA in cells. If you have HRD, your tumour cannot fix DNA breaks. PARP inhibitors make this problem worse for cancer cells. The cells die because they cannot repair themselves. These drugs help people with BRCA mutations or other HRD-positive tumours.
Here are ways PARP inhibitors help in HRD-positive cancers:
People with BRCA mutations often do well with PARP inhibitors.
Tumours with BRCA1 or RAD51C inactivation, even by promoter methylation, also respond well.
These drugs work best in ovarian cancer. They also help in breast and prostate cancer.
Recent trials show PARP inhibitors like niraparib work well in HRD-positive ovarian tumours. Some studies test PARP inhibitors with other therapies to get better results.
Therapy Type | Effectiveness in HRD-positive Tumors | Response Rate | Safety Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
PARP Inhibitors (Niraparib) | Work well, especially in ovarian cancer | 73.6% | Good |
Combination with eTregs | May help even more | N/A | N/A |
Note: Targeted therapies like PARP inhibitors give you more choices. They may help you get better results if your tumour has hrd.
HRD testing helps patients get better outcomes. If you have an HRD-positive tumour, you may live longer without your cancer getting worse. This is called progression-free survival. Studies show HRD-positive ovarian cancer patients who get PARP inhibitors like niraparib do better than those who do not.
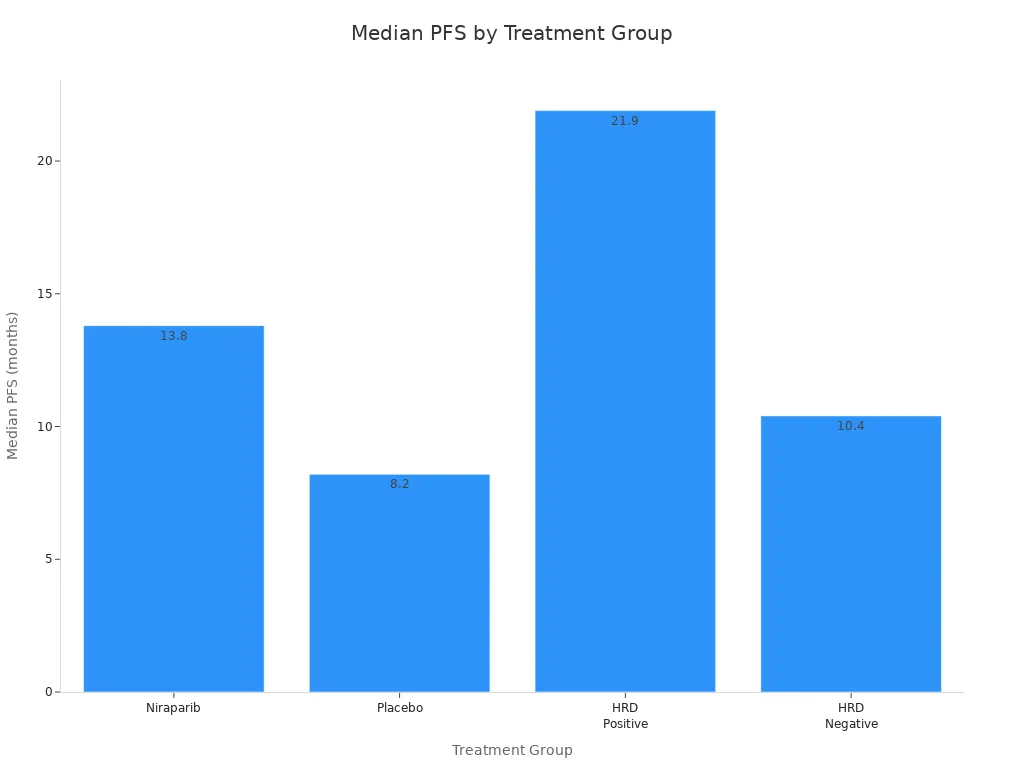
Here is a table showing how HRD status changes outcomes:
Treatment Group | Median PFS (months) | HR (Hazard Ratio) | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
Niraparib | 13.8 | 0.62 | 0.50–0.76 |
Placebo | 8.2 | N/A | N/A |
HRD Positive | 21.9 | 0.43 | 0.31–0.59 |
HRD Negative | 10.4 | N/A | N/A |
You can see the difference in this chart:
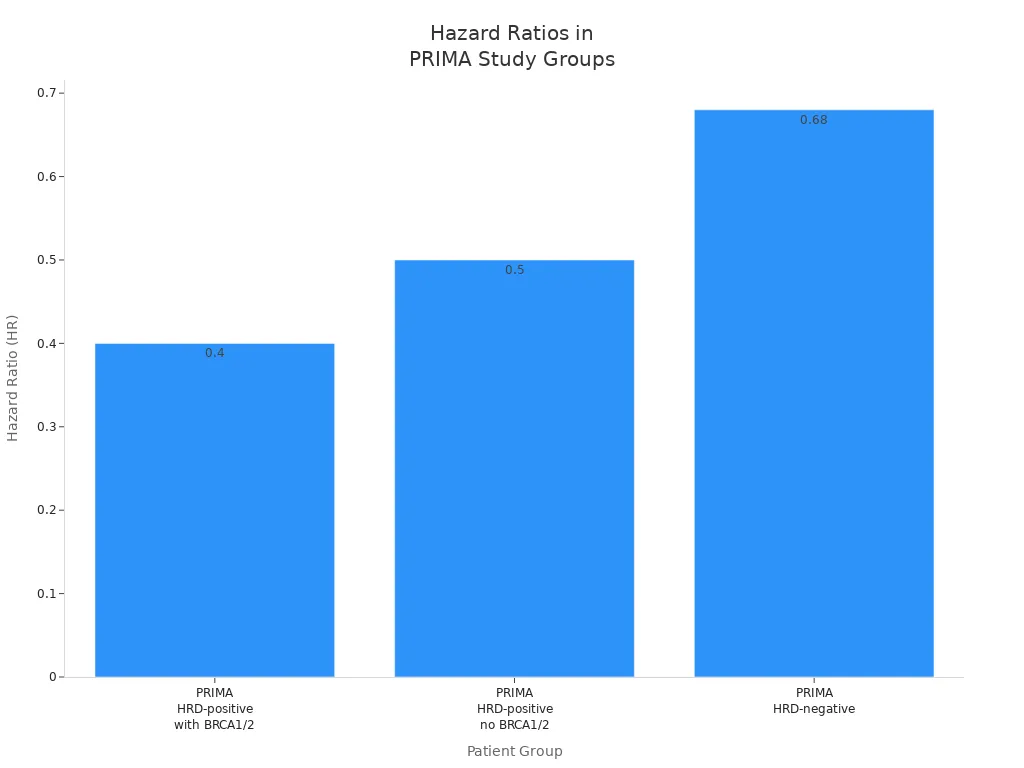
Big studies like PRIMA and PAOLA-1 show HRD-positive patients get the most help from PARP inhibitors and other targeted therapies. These studies include people with and without BRCA mutations. The results show HRD testing helps many patients with ovarian cancer and other cancers.
Study | Patient Group | Treatment | Median PFS Improvement | Hazard Ratio (HR) | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
PRIMA | HRD-positive with somatic BRCA1/2 | Niraparib maintenance | Strong response | 0.4 | (0.27, 0.62) |
PRIMA | HRD-positive without somatic BRCA1/2 | Niraparib maintenance | PFS benefit | 0.5 | (0.31, 0.83) |
PRIMA | HRD-negative | Niraparib maintenance | PFS benefit | 0.68 | (0.49, 0.94) |
PAOLA-1 | HRD-positive | Bevacizumab + Olaparib | 19.5 months | N/A | N/A |
PAOLA-1 | HRD-positive without somatic BRCA1/2 | Bevacizumab + Olaparib | 11.5 months | N/A | N/A |
Callout: HRD testing gives you and your doctor key information. It helps you get the right treatment and improves your chances for better results.
You help your cancer care by learning about HRD testing. This test helps you and your doctor pick the best treatment. It is very important for breast and ovarian cancers. Getting correct results can help you do better. Big groups say to use good lab standards and best practices. You can find guides and resources to help you make choices.
Talk to your care team about testing options.
Look for easy-to-read materials about cancer biomarkers.
Challenge | What to Know |
|---|---|
Access | Some places do not have testing |
Cost | Testing does not cost too much |
Patient Factors | Age and health can change decisions |
Remember: Good testing helps you get care that fits you. It gives you more ways to treat your cancer.
HRD shows your tumor cannot fix DNA damage. You may get more choices for targeted therapies like PARP inhibitors. Doctors use your HRD status to help pick the best treatment plan.
Labs use reference standards. These standards act like real tumor samples. They help labs check their tests and keep results reliable.
You can get HRD testing for many cancers. Doctors often use it for ovarian, breast, and prostate cancers. Some other cancers may also show HRD, so ask your care team about your options.
You should talk to your doctor. Ask if your tumor type benefits from HRD testing. Make sure your tissue sample is good quality. This helps you get the most accurate results.
A negative HRD result means your tumor repairs DNA better. You may not respond as well to PARP inhibitors. Your doctor can help you find other treatment options.
This category is empty.