- Home
- Products
- Services
- Resources
- About Us
- News
- Contact

loading
CBPL0007
CBPL0007
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
Description
This product covers 20 insertion sites, coming from 20 genes on 11 different chromosomes, with an integration frequency of 5%.
Through NGS (capture probe sequencing) technology, combined with bioinformatics analysis methods, genes with more than 1000× reads were selected for Sanger and ddPCR verification, and the integration frequency was detected by ddPCR. Multiple methods were combined to accurately locate the insertion site and integration frequency of the lentivirus.
General information
Name | Lentivirus polyclonal multi-integration site reference - 5% |
Cat. No. | CBPL0007 |
Format | Genomic DNA |
Size | 1ug |
Storage Conditions | 2~8℃ |
Expiry | 36 months from the date of manufacture |
Detection Methods
Currently, the main platform for detecting lentiviral integration sites is high-depth sequencing (NGS).
| Methods | Features |
| nrLAM-PCR | 1. Single-stranded linker, low connection effciency 2. Complex process, high cost 3. No need to interrupt the genome |
| LAM-PCR | 1. Single-stranded linker, low connection effciency 2. Complex process, high cost 3. Enzyme digestion is used for genome interruption, whichhas site recognition preference, will introduce technical errors, and has certain limitations for identifying all insertion sites |
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) | 1. Requires a large amount of data, high sequencing cost 2. No need to design primers |
| LM-PCR | 1. Ultrasonic physical random interruption, no preference 2. Compared with WGS method, it does not require a largeamount of data 3. Double-stranded linker, high connection effciency |
| LTA-PCR | 1. Proven ISA detection method 2. Has excellent detection performance in many vral vectors |
After comprehensive consideration,CB-Gene selected multiple methods (capture probe sequencing + sanger + ddPCR) for verification to fully verify the accuracy of the standard. During the verification process, the accuracy of capture probe sequencing technology for lentiviral integration site detection was well verified.
Ⅳ.Integration sites(hg19)
Chromosome location | Breakpoint location | Gene | Frequency |
chr2 | 128744988 | SAP130 | 5% |
chr2 | 213888416 | IKZF2 | 5% |
chr3 | 4871944 | ITPR1 | 5% |
chr3 | 43344305 | SNRK | 5% |
chr4 | 288630 | ZNF732 | 5% |
chr4 | 16184544 | TAPT1 | 5% |
chr6 | 74230646 | EEF1A1 | 5% |
chr8 | 145512905 | BOP1 | 5% |
chr8 | 145523573 | HSF1 | 5% |
chr9 | 130845722 | SLC25A25 | 5% |
chr9 | 33997906 | UBAP2 | 5% |
chr9 | 131719784 | NUP188 | 5% |
chr9 | 115151308 | HSDL2 | 5% |
chr9 | 139798150 | TRAF2 | 5% |
chr16 | 47285195 | ITFG1 | 5% |
chr17 | 18494286 | CCDC144B | 5% |
chr19 | 56328752 | NLRP11 | 5% |
chr19 | 55914181 | UBE2S | 5% |
chr22 | 50808061 | PPP6R2 | 5% |
chrX | 38435241 | TSPAN7 | 5% |
Ⅴ.Representative Data
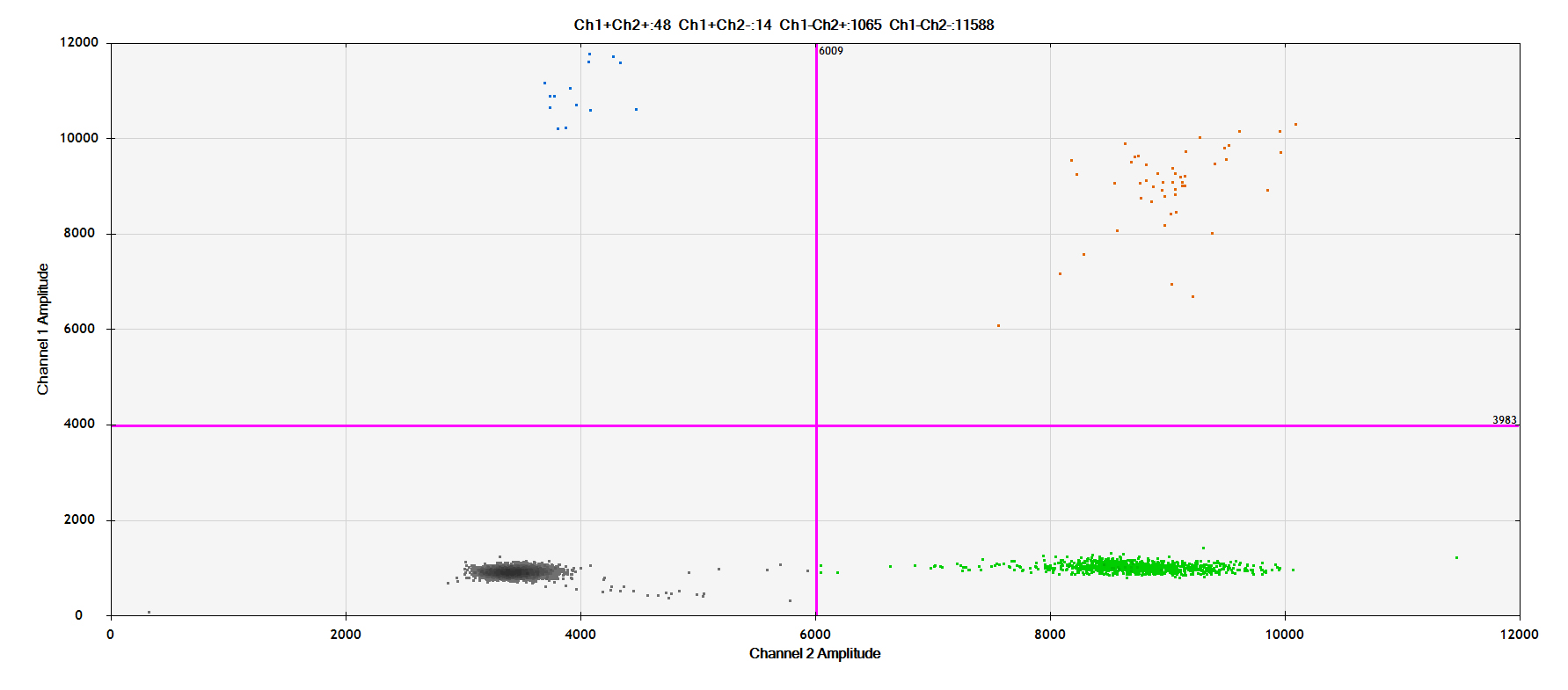
Case presentation - 5% chr3: 4871944 ITPR1 Four test results:
LM-PCR:
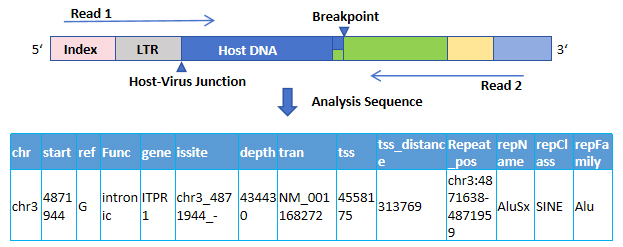
NGS:

Sanger:
3'LTR+ITPR1 chr3_4871940 |
ITPR1 chr3_4871944+5'LTR |
DPCR:
Ⅵ.Related Products List
Product | Catalog No. | Description | Details |
Lentiviral Vector Integration Site Reference Standard | CBPL0002 | Contains multiple insertion sites |
|
Lentiviral Vector Integration Site Reference Standard III (Single site) | CBPL0004 | Contains one insertion site |
|
Lentiviral Vector Integration Site Reference Standard II (Single site) | CBPL0003 | Contains one insertion site |
|
Lentiviral Integration Site Analysis Reference Reagent IV (Contains Sex Chromosome Insertion) | CBPL0005 | including one sex chromosome site | |
Lentivirus Integration Site Analysis Negative Reference Reagent | CBPL0006 | Negative control | |
Lentivirus polyclonal multi-integration site reference - 2% | CBPL0008 | Covering 20 insertion sites |
|
Description
This product covers 20 insertion sites, coming from 20 genes on 11 different chromosomes, with an integration frequency of 5%.
Through NGS (capture probe sequencing) technology, combined with bioinformatics analysis methods, genes with more than 1000× reads were selected for Sanger and ddPCR verification, and the integration frequency was detected by ddPCR. Multiple methods were combined to accurately locate the insertion site and integration frequency of the lentivirus.
General information
Name | Lentivirus polyclonal multi-integration site reference - 5% |
Cat. No. | CBPL0007 |
Format | Genomic DNA |
Size | 1ug |
Storage Conditions | 2~8℃ |
Expiry | 36 months from the date of manufacture |
Detection Methods
Currently, the main platform for detecting lentiviral integration sites is high-depth sequencing (NGS).
| Methods | Features |
| nrLAM-PCR | 1. Single-stranded linker, low connection effciency 2. Complex process, high cost 3. No need to interrupt the genome |
| LAM-PCR | 1. Single-stranded linker, low connection effciency 2. Complex process, high cost 3. Enzyme digestion is used for genome interruption, whichhas site recognition preference, will introduce technical errors, and has certain limitations for identifying all insertion sites |
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) | 1. Requires a large amount of data, high sequencing cost 2. No need to design primers |
| LM-PCR | 1. Ultrasonic physical random interruption, no preference 2. Compared with WGS method, it does not require a largeamount of data 3. Double-stranded linker, high connection effciency |
| LTA-PCR | 1. Proven ISA detection method 2. Has excellent detection performance in many vral vectors |
After comprehensive consideration,CB-Gene selected multiple methods (capture probe sequencing + sanger + ddPCR) for verification to fully verify the accuracy of the standard. During the verification process, the accuracy of capture probe sequencing technology for lentiviral integration site detection was well verified.
Ⅳ.Integration sites(hg19)
Chromosome location | Breakpoint location | Gene | Frequency |
chr2 | 128744988 | SAP130 | 5% |
chr2 | 213888416 | IKZF2 | 5% |
chr3 | 4871944 | ITPR1 | 5% |
chr3 | 43344305 | SNRK | 5% |
chr4 | 288630 | ZNF732 | 5% |
chr4 | 16184544 | TAPT1 | 5% |
chr6 | 74230646 | EEF1A1 | 5% |
chr8 | 145512905 | BOP1 | 5% |
chr8 | 145523573 | HSF1 | 5% |
chr9 | 130845722 | SLC25A25 | 5% |
chr9 | 33997906 | UBAP2 | 5% |
chr9 | 131719784 | NUP188 | 5% |
chr9 | 115151308 | HSDL2 | 5% |
chr9 | 139798150 | TRAF2 | 5% |
chr16 | 47285195 | ITFG1 | 5% |
chr17 | 18494286 | CCDC144B | 5% |
chr19 | 56328752 | NLRP11 | 5% |
chr19 | 55914181 | UBE2S | 5% |
chr22 | 50808061 | PPP6R2 | 5% |
chrX | 38435241 | TSPAN7 | 5% |
Ⅴ.Representative Data
Case presentation - 5% chr3: 4871944 ITPR1 Four test results:
LM-PCR:

NGS:

Sanger:
3'LTR+ITPR1 chr3_4871940 |
ITPR1 chr3_4871944+5'LTR |
DPCR:

Ⅵ.Related Products List
Product | Catalog No. | Description | Details |
Lentiviral Vector Integration Site Reference Standard | CBPL0002 | Contains multiple insertion sites |
|
Lentiviral Vector Integration Site Reference Standard III (Single site) | CBPL0004 | Contains one insertion site |
|
Lentiviral Vector Integration Site Reference Standard II (Single site) | CBPL0003 | Contains one insertion site |
|
Lentiviral Integration Site Analysis Reference Reagent IV (Contains Sex Chromosome Insertion) | CBPL0005 | including one sex chromosome site | |
Lentivirus Integration Site Analysis Negative Reference Reagent | CBPL0006 | Negative control | |
Lentivirus polyclonal multi-integration site reference - 2% | CBPL0008 | Covering 20 insertion sites |
|
Detection Methods
Currently, the main platform for detecting lentiviral integration sites is high-depth sequencing (NGS).
Methods | Features |
nrLAM-PCR | 1. Single-stranded linker, low connection effciency 2. Complex process, high cost 3. No need to interrupt the genome |
LAM-PCR | 1. Single-stranded linker, low connection effciency 2. Complex process, high cost 3. Enzyme digestion is used for genome interruption, whichhas site recognition preference, will introduce technical errors, and has certain limitations for identifying all insertion sites |
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) | 1. Requires a large amount of data, high sequencing cost 2. No need to design primers |
LM-PCR | 1. Ultrasonic physical random interruption, no preference 2. Compared with WGS method, it does not require a largeamount of data 3. Double-stranded linker, high connection effciency |
LTA-PCR | 1. Proven ISA detection method 2. Has excellent detection performance in many vral vectors |
After comprehensive consideration,CB-Gene selected multiple methods (capture probe sequencing + sanger + ddPCR) for verification to fully verify the accuracy of the standard. During the verification process, the accuracy of capture probe sequencing technology for lentiviral integration site detection was well verified.
Detection Methods
Currently, the main platform for detecting lentiviral integration sites is high-depth sequencing (NGS).
Methods | Features |
nrLAM-PCR | 1. Single-stranded linker, low connection effciency 2. Complex process, high cost 3. No need to interrupt the genome |
LAM-PCR | 1. Single-stranded linker, low connection effciency 2. Complex process, high cost 3. Enzyme digestion is used for genome interruption, whichhas site recognition preference, will introduce technical errors, and has certain limitations for identifying all insertion sites |
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) | 1. Requires a large amount of data, high sequencing cost 2. No need to design primers |
LM-PCR | 1. Ultrasonic physical random interruption, no preference 2. Compared with WGS method, it does not require a largeamount of data 3. Double-stranded linker, high connection effciency |
LTA-PCR | 1. Proven ISA detection method 2. Has excellent detection performance in many vral vectors |
After comprehensive consideration,CB-Gene selected multiple methods (capture probe sequencing + sanger + ddPCR) for verification to fully verify the accuracy of the standard. During the verification process, the accuracy of capture probe sequencing technology for lentiviral integration site detection was well verified.
Ⅳ.Integration sites(hg19)
Chromosome location | Breakpoint location | Gene | Frequency |
chr2 | 128744988 | SAP130 | 5% |
chr2 | 213888416 | IKZF2 | 5% |
chr3 | 4871944 | ITPR1 | 5% |
chr3 | 43344305 | SNRK | 5% |
chr4 | 288630 | ZNF732 | 5% |
chr4 | 16184544 | TAPT1 | 5% |
chr6 | 74230646 | EEF1A1 | 5% |
chr8 | 145512905 | BOP1 | 5% |
chr8 | 145523573 | HSF1 | 5% |
chr9 | 130845722 | SLC25A25 | 5% |
chr9 | 33997906 | UBAP2 | 5% |
chr9 | 131719784 | NUP188 | 5% |
chr9 | 115151308 | HSDL2 | 5% |
chr9 | 139798150 | TRAF2 | 5% |
chr16 | 47285195 | ITFG1 | 5% |
chr17 | 18494286 | CCDC144B | 5% |
chr19 | 56328752 | NLRP11 | 5% |
chr19 | 55914181 | UBE2S | 5% |
chr22 | 50808061 | PPP6R2 | 5% |
chrX | 38435241 | TSPAN7 | 5% |
Ⅳ.Integration sites(hg19)
Chromosome location | Breakpoint location | Gene | Frequency |
chr2 | 128744988 | SAP130 | 5% |
chr2 | 213888416 | IKZF2 | 5% |
chr3 | 4871944 | ITPR1 | 5% |
chr3 | 43344305 | SNRK | 5% |
chr4 | 288630 | ZNF732 | 5% |
chr4 | 16184544 | TAPT1 | 5% |
chr6 | 74230646 | EEF1A1 | 5% |
chr8 | 145512905 | BOP1 | 5% |
chr8 | 145523573 | HSF1 | 5% |
chr9 | 130845722 | SLC25A25 | 5% |
chr9 | 33997906 | UBAP2 | 5% |
chr9 | 131719784 | NUP188 | 5% |
chr9 | 115151308 | HSDL2 | 5% |
chr9 | 139798150 | TRAF2 | 5% |
chr16 | 47285195 | ITFG1 | 5% |
chr17 | 18494286 | CCDC144B | 5% |
chr19 | 56328752 | NLRP11 | 5% |
chr19 | 55914181 | UBE2S | 5% |
chr22 | 50808061 | PPP6R2 | 5% |
chrX | 38435241 | TSPAN7 | 5% |
Ⅴ.Representative Data
Case presentation - 5% chr3: 4871944 ITPR1 Four test results:
LM-PCR:

NGS:

Sanger:
3'LTR+ITPR1 chr3_4871940 |
ITPR1 chr3_4871944+5'LTR |
DPCR:

Ⅴ.Representative Data
Case presentation - 5% chr3: 4871944 ITPR1 Four test results:
LM-PCR:

NGS:

Sanger:
3'LTR+ITPR1 chr3_4871940 |
ITPR1 chr3_4871944+5'LTR |
DPCR:

Ⅵ.Related Products List
Product | CatalogNo. | Description | Details |
Lentiviral Vector Integration Site Reference Standard | CBPL0002 | Contains multiple insertion sites |
|
Lentiviral Vector Integration Site Reference Standard III (Single site) | CBPL0004 | Contains one insertion site |
|
Lentiviral Vector Integration Site Reference Standard II (Single site) | CBPL0003 | Contains one insertion site |
|
Lentiviral Integration Site Analysis Reference Reagent IV (Contains Sex Chromosome Insertion) | CBPL0005 | including one sex chromosome site | |
Lentivirus Integration Site Analysis Negative Reference Reagent | CBPL0006 | Negative control | |
Lentivirus polyclonal multi-integration site reference - 2% | CBPL0008 | Covering 20 insertion sites |
|
Ⅵ.Related Products List
Product | CatalogNo. | Description | Details |
Lentiviral Vector Integration Site Reference Standard | CBPL0002 | Contains multiple insertion sites |
|
Lentiviral Vector Integration Site Reference Standard III (Single site) | CBPL0004 | Contains one insertion site |
|
Lentiviral Vector Integration Site Reference Standard II (Single site) | CBPL0003 | Contains one insertion site |
|
Lentiviral Integration Site Analysis Reference Reagent IV (Contains Sex Chromosome Insertion) | CBPL0005 | including one sex chromosome site | |
Lentivirus Integration Site Analysis Negative Reference Reagent | CBPL0006 | Negative control | |
Lentivirus polyclonal multi-integration site reference - 2% | CBPL0008 | Covering 20 insertion sites |
|