- Home
- Products
- Services
- Resources
- About Us
- News
- Contact

loading
CBP90001
CBP90001
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
Gene fusions (e.g., EML4-ALK, BCR-ABL1) drive malignant blood cancers and solid tumors, making them critical biomarkers for targeted therapy. The Panel-Ref® RNA-Fusion Cocktail Control (CBP90001) is a high-quality QC material upgraded in 2021 to include 22 fusion sites (from 11) and FFPE slide format (replacing RNA solution) to better simulate clinical sample processing (e.g., RNA extraction). It contains 11 clinically relevant fusion transcripts, all quantified via ddPCR for accuracy.
The FFPE slide format replicates real-world clinical workflows (e.g., formalin fixation, RNA extraction), helping labs validate assay performance through every step—unlike liquid RNA standards.
Including 11 high-impact fusions (e.g., NTRK, RET, ROS1 fusions), it supports validation of NGS/ddPCR-based fusion detection assays for lung, breast, and hematologic cancers.
Each fusion’s copy number is calibrated via ddPCR, ensuring accurate quantification for testing assay sensitivity (e.g., detecting low-abundance fusion transcripts) and reproducibility.
Packaged in RNase-free buffer with high RNQ value, it maintains RNA integrity during storage and handling, avoiding false negatives from degraded samples.
We advise on fusion selection (e.g., prioritizing EML4-ALK for lung cancer research) and format (RNA solution vs. FFPE) based on your assay platform (e.g., RNA-seq, RT-ddPCR).
RNA is shipped on dry ice to preserve integrity; FFPE slides include handling instructions to prevent RNA degradation during processing.
Our team provides protocols for FFPE RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and fusion detection, helping resolve issues like low yield or inconsistent results.
We share ddPCR calibration data to help you cross-verify your assay’s quantification accuracy for each fusion transcript.
Gene fusion detection requires robust QC to avoid misdiagnosing patients. This standard’s FFPE format, ddPCR validation, and comprehensive fusion coverage make it ideal for optimizing RNA-seq/ddPCR workflows, monitoring daily test performance, and ensuring reliable biomarker detection. Contact us to streamline your fusion testing QC.
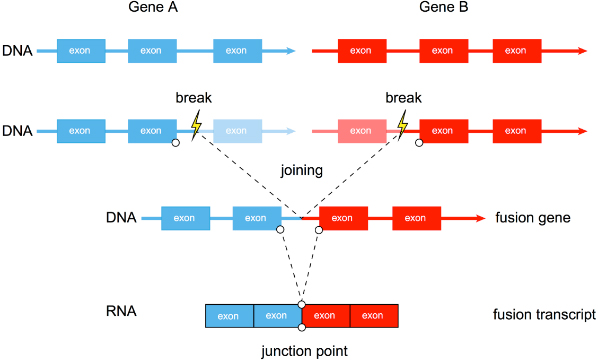
There are three main mechanisms for gene fusion, as shown in the following figure:
There are three common mechanisms of gene fusion:
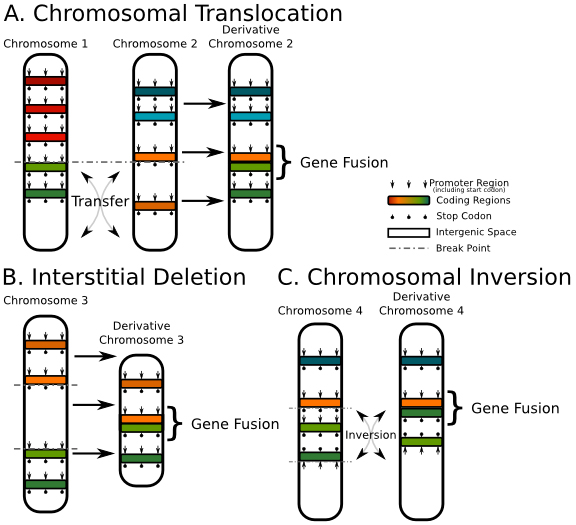
1) Chromosomal Translocation. As shown in Figure A above, the two segments on chromosomes 1 and 2 cross and exchange, resulting in the fusion of the light green gene on chromosome 1 and the orange gene on chromosome 2;
2) Interstitial deletion. As shown in the figure above, the segment between the orange gene and the light green gene on chromosome 3 is deleted, eventually resulting in the fusion of the two genes;
3) Chromosomal Inversion. For example, the segment between the orange gene and the dark green gene on chromosome 4 is inverted, eventually resulting in the fusion of the orange gene and the light green gene.
General information
Name | Panel-Ref® RNA-Fusion Cocktail Control |
Cat. No. | CBP90001 |
Format | RNA |
Buffer | RNase-free H2O |
Conc.(Qubit3.0) | 60ng/uL |
OD260/OD280(1.8~2.1) | 1.98 |
RNQ Value(>9 (Qsep) | >9 |
Copy Number(DdPCR) | Below |
Description | RNA containing 11 fusion mutations, all quantified by dPCR |
Size | 1ug |
Intended Use | Research Use Only |
Storage Conditions | -90℃~70℃ |
Expiry | 12 months from the date of manufacture |
Detailed Data
Name | Left Gene | Left Breakpoint | Right Gene | Right Breakpoint | Copies/ng |
CCDC6-RET Fusion (E1-E12) | CCDC6(E1) | chr10:61665880:- | RET(E12) | chr10:43612032:+ | COA download |
EML4-ALK Fusion (E13-E20) | EML4(E13) | chr2:42522656:+ | ALK(A20) | chr2:29446394:- | COA download |
ETV6-NTRK3 Fusion (E5-E15) | ETV6(E5) | chr12:12022903:+ | NTRK3(E15) | chr15:88483984:- | COA download |
KIF5B-RET Fusion (E15-E12) | KIF5B(E15) | chr10:32317356:- | RET(E12) | chr10:43612032:+ | COA download |
NPM1-ALK Fusion (E4-E20) | NPM1(E4) | chr5:170818803:+ | ALK(E20) | chr2:29446394:- | COA download |
SLC34A2-ROS1 Fusion (E4-E32) | SLC34A2(E4) | chr4:25665952:+ | ROS1(E32) | chr6:117650609:- | COA download |
TPM3-NTRK1 Fusion (E7-E9) | TPM3(E7) | chr1:154142876:- | NTRK1(E9) | chr1:156844363:+ | COA download |
FGFR3-TACC3 (E17-E11) | FGFR3(E17) | chr4:1808661:+ | TACC3(E11) | chr4:1741429:+ | COA download |
MET exon14 Skiping (E13-E15) | MET(E13) | chr7:116411708:+ | MET(E15) | chr7:116414935:+ | COA download |
BCR-ABL1 (E14-E2) | BCR(E14) | chr22:23632600:+ | ABL1(E2) | chr9:133729451:+ | COA download |
CD74-ROS1(E6-E34) | CD74(E6) | chr5:149784243:- | ROS1(E34) | chr6:117645578:- | COA download |
Gene fusions (e.g., EML4-ALK, BCR-ABL1) drive malignant blood cancers and solid tumors, making them critical biomarkers for targeted therapy. The Panel-Ref® RNA-Fusion Cocktail Control (CBP90001) is a high-quality QC material upgraded in 2021 to include 22 fusion sites (from 11) and FFPE slide format (replacing RNA solution) to better simulate clinical sample processing (e.g., RNA extraction). It contains 11 clinically relevant fusion transcripts, all quantified via ddPCR for accuracy.
The FFPE slide format replicates real-world clinical workflows (e.g., formalin fixation, RNA extraction), helping labs validate assay performance through every step—unlike liquid RNA standards.
Including 11 high-impact fusions (e.g., NTRK, RET, ROS1 fusions), it supports validation of NGS/ddPCR-based fusion detection assays for lung, breast, and hematologic cancers.
Each fusion’s copy number is calibrated via ddPCR, ensuring accurate quantification for testing assay sensitivity (e.g., detecting low-abundance fusion transcripts) and reproducibility.
Packaged in RNase-free buffer with high RNQ value, it maintains RNA integrity during storage and handling, avoiding false negatives from degraded samples.
We advise on fusion selection (e.g., prioritizing EML4-ALK for lung cancer research) and format (RNA solution vs. FFPE) based on your assay platform (e.g., RNA-seq, RT-ddPCR).
RNA is shipped on dry ice to preserve integrity; FFPE slides include handling instructions to prevent RNA degradation during processing.
Our team provides protocols for FFPE RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and fusion detection, helping resolve issues like low yield or inconsistent results.
We share ddPCR calibration data to help you cross-verify your assay’s quantification accuracy for each fusion transcript.
Gene fusion detection requires robust QC to avoid misdiagnosing patients. This standard’s FFPE format, ddPCR validation, and comprehensive fusion coverage make it ideal for optimizing RNA-seq/ddPCR workflows, monitoring daily test performance, and ensuring reliable biomarker detection. Contact us to streamline your fusion testing QC.

There are three main mechanisms for gene fusion, as shown in the following figure:

There are three common mechanisms of gene fusion:
1) Chromosomal Translocation. As shown in Figure A above, the two segments on chromosomes 1 and 2 cross and exchange, resulting in the fusion of the light green gene on chromosome 1 and the orange gene on chromosome 2;
2) Interstitial deletion. As shown in the figure above, the segment between the orange gene and the light green gene on chromosome 3 is deleted, eventually resulting in the fusion of the two genes;
3) Chromosomal Inversion. For example, the segment between the orange gene and the dark green gene on chromosome 4 is inverted, eventually resulting in the fusion of the orange gene and the light green gene.
General information
Name | Panel-Ref® RNA-Fusion Cocktail Control |
Cat. No. | CBP90001 |
Format | RNA |
Buffer | RNase-free H2O |
Conc.(Qubit3.0) | 60ng/uL |
OD260/OD280(1.8~2.1) | 1.98 |
RNQ Value(>9 (Qsep) | >9 |
Copy Number(DdPCR) | Below |
Description | RNA containing 11 fusion mutations, all quantified by dPCR |
Size | 1ug |
Intended Use | Research Use Only |
Storage Conditions | -90℃~70℃ |
Expiry | 12 months from the date of manufacture |
Detailed Data
Name | Left Gene | Left Breakpoint | Right Gene | Right Breakpoint | Copies/ng |
CCDC6-RET Fusion (E1-E12) | CCDC6(E1) | chr10:61665880:- | RET(E12) | chr10:43612032:+ | COA download |
EML4-ALK Fusion (E13-E20) | EML4(E13) | chr2:42522656:+ | ALK(A20) | chr2:29446394:- | COA download |
ETV6-NTRK3 Fusion (E5-E15) | ETV6(E5) | chr12:12022903:+ | NTRK3(E15) | chr15:88483984:- | COA download |
KIF5B-RET Fusion (E15-E12) | KIF5B(E15) | chr10:32317356:- | RET(E12) | chr10:43612032:+ | COA download |
NPM1-ALK Fusion (E4-E20) | NPM1(E4) | chr5:170818803:+ | ALK(E20) | chr2:29446394:- | COA download |
SLC34A2-ROS1 Fusion (E4-E32) | SLC34A2(E4) | chr4:25665952:+ | ROS1(E32) | chr6:117650609:- | COA download |
TPM3-NTRK1 Fusion (E7-E9) | TPM3(E7) | chr1:154142876:- | NTRK1(E9) | chr1:156844363:+ | COA download |
FGFR3-TACC3 (E17-E11) | FGFR3(E17) | chr4:1808661:+ | TACC3(E11) | chr4:1741429:+ | COA download |
MET exon14 Skiping (E13-E15) | MET(E13) | chr7:116411708:+ | MET(E15) | chr7:116414935:+ | COA download |
BCR-ABL1 (E14-E2) | BCR(E14) | chr22:23632600:+ | ABL1(E2) | chr9:133729451:+ | COA download |
CD74-ROS1(E6-E34) | CD74(E6) | chr5:149784243:- | ROS1(E34) | chr6:117645578:- | COA download |
General Information
Name | Panel-Ref® RNA-Fusion Cocktail Control |
Cat. No. | CBP90001 |
Format | RNA |
Buffer | RNase-free H2O |
Conc.(Qubit3.0) | 60ng/uL |
OD260/OD280(1.8~2.1) | 1.98 |
RNQ Value(>9 (Qsep) | >9 |
Copy Number(DdPCR) | Below |
Description | RNA containing 11 fusion mutations, all quantified by dPCR |
Size | 1ug |
Intended Use | Research Use Only |
Storage Conditions | -90℃~70℃ |
Expiry | 12 months from the date of manufacture |
General Information
Name | Panel-Ref® RNA-Fusion Cocktail Control |
Cat. No. | CBP90001 |
Format | RNA |
Buffer | RNase-free H2O |
Conc.(Qubit3.0) | 60ng/uL |
OD260/OD280(1.8~2.1) | 1.98 |
RNQ Value(>9 (Qsep) | >9 |
Copy Number(DdPCR) | Below |
Description | RNA containing 11 fusion mutations, all quantified by dPCR |
Size | 1ug |
Intended Use | Research Use Only |
Storage Conditions | -90℃~70℃ |
Expiry | 12 months from the date of manufacture |
Detection Methods
The identification of gene fusion can be based on whole-genome sequencing data (WGS), transcriptome sequencing data (RNA-seq), or a combination of the two technologies.
Gene fusions identified by whole-genome sequencing can basically be determined to be caused by some mutations at the genomic level, but without transcriptome sequencing data, it is impossible to accurately determine whether the new gene produced after the fusion can be expressed, or the level of expression.
Gene fusions identified by transcriptome sequencing data can clearly be expressed gene fusions, but it is impossible to completely determine whether they are caused by genomic mutations or RNA fusions after transcription of two different genes.
Therefore, if conditions permit, combining whole-genome sequencing (WGS, or panel) and transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) to identify gene fusions can obtain more accurate identification results.
Detection Methods
The identification of gene fusion can be based on whole-genome sequencing data (WGS), transcriptome sequencing data (RNA-seq), or a combination of the two technologies.
Gene fusions identified by whole-genome sequencing can basically be determined to be caused by some mutations at the genomic level, but without transcriptome sequencing data, it is impossible to accurately determine whether the new gene produced after the fusion can be expressed, or the level of expression.
Gene fusions identified by transcriptome sequencing data can clearly be expressed gene fusions, but it is impossible to completely determine whether they are caused by genomic mutations or RNA fusions after transcription of two different genes.
Therefore, if conditions permit, combining whole-genome sequencing (WGS, or panel) and transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) to identify gene fusions can obtain more accurate identification results.
Detailed Data
Name | Left Gene | Left Breakpoint | Right Gene | Right Breakpoint | Copies/ng |
CCDC6-RET Fusion (E1-E12) | CCDC6(E1) | chr10:61665880:- | RET(E12) | chr10:43612032:+ | COA download |
EML4-ALK Fusion (E13-E20) | EML4(E13) | chr2:42522656:+ | ALK(A20) | chr2:29446394:- | COA download |
ETV6-NTRK3 Fusion (E5-E15) | ETV6(E5) | chr12:12022903:+ | NTRK3(E15) | chr15:88483984:- | COA download |
KIF5B-RET Fusion (E15-E12) | KIF5B(E15) | chr10:32317356:- | RET(E12) | chr10:43612032:+ | COA download |
NPM1-ALK Fusion (E4-E20) | NPM1(E4) | chr5:170818803:+ | ALK(E20) | chr2:29446394:- | COA download |
SLC34A2-ROS1 Fusion (E4-E32) | SLC34A2(E4) | chr4:25665952:+ | ROS1(E32) | chr6:117650609:- | COA download |
TPM3-NTRK1 Fusion (E7-E9) | TPM3(E7) | chr1:154142876:- | NTRK1(E9) | chr1:156844363:+ | COA download |
FGFR3-TACC3 (E17-E11) | FGFR3(E17) | chr4:1808661:+ | TACC3(E11) | chr4:1741429:+ | COA download |
MET exon14 Skiping (E13-E15) | MET(E13) | chr7:116411708:+ | MET(E15) | chr7:116414935:+ | COA download |
BCR-ABL1 (E14-E2) | BCR(E14) | chr22:23632600:+ | ABL1(E2) | chr9:133729451:+ | COA download |
CD74-ROS1(E6-E34) | CD74(E6) | chr5:149784243:- | ROS1(E34) | chr6:117645578:- | COA download |
Detailed Data
Name | Left Gene | Left Breakpoint | Right Gene | Right Breakpoint | Copies/ng |
CCDC6-RET Fusion (E1-E12) | CCDC6(E1) | chr10:61665880:- | RET(E12) | chr10:43612032:+ | COA download |
EML4-ALK Fusion (E13-E20) | EML4(E13) | chr2:42522656:+ | ALK(A20) | chr2:29446394:- | COA download |
ETV6-NTRK3 Fusion (E5-E15) | ETV6(E5) | chr12:12022903:+ | NTRK3(E15) | chr15:88483984:- | COA download |
KIF5B-RET Fusion (E15-E12) | KIF5B(E15) | chr10:32317356:- | RET(E12) | chr10:43612032:+ | COA download |
NPM1-ALK Fusion (E4-E20) | NPM1(E4) | chr5:170818803:+ | ALK(E20) | chr2:29446394:- | COA download |
SLC34A2-ROS1 Fusion (E4-E32) | SLC34A2(E4) | chr4:25665952:+ | ROS1(E32) | chr6:117650609:- | COA download |
TPM3-NTRK1 Fusion (E7-E9) | TPM3(E7) | chr1:154142876:- | NTRK1(E9) | chr1:156844363:+ | COA download |
FGFR3-TACC3 (E17-E11) | FGFR3(E17) | chr4:1808661:+ | TACC3(E11) | chr4:1741429:+ | COA download |
MET exon14 Skiping (E13-E15) | MET(E13) | chr7:116411708:+ | MET(E15) | chr7:116414935:+ | COA download |
BCR-ABL1 (E14-E2) | BCR(E14) | chr22:23632600:+ | ABL1(E2) | chr9:133729451:+ | COA download |
CD74-ROS1(E6-E34) | CD74(E6) | chr5:149784243:- | ROS1(E34) | chr6:117645578:- | COA download |
Product Application
1.Widely used in customers’ quality control testing
2.Quality assessment for monitoring NGS- or dPCR-based tumor testing workflows
Product Application
1.Widely used in customers’ quality control testing
2.Quality assessment for monitoring NGS- or dPCR-based tumor testing workflows