- Home
- Products
- Services
- Resources
- About Us
- News
- Contact

loading
CBP90040
CBP90040
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
Package-Ref™ MRD Cocktail Reference Standard is a specialized ctDNA-based reference material tailored for pan-tumor MRD detection quality control. MRD—defined as residual tumor cells or molecular markers remaining post-treatment—requires ultra-sensitive detection to predict recurrence and guide clinical decisions. This product addresses the core pain point of ultra-low frequency mutation detection, with a minimum detectable mutation frequency of 0.005% (5 mutant molecules per 100,000 total molecules), enabling validation of even the most sensitive MRD assays.
Crafted from ultrasonicated ctDNA (to mimic real-world clinical samples), the standard is supplied in a ready-to-use format, eliminating the need for complex preprocessing and ensuring consistency across experiments.
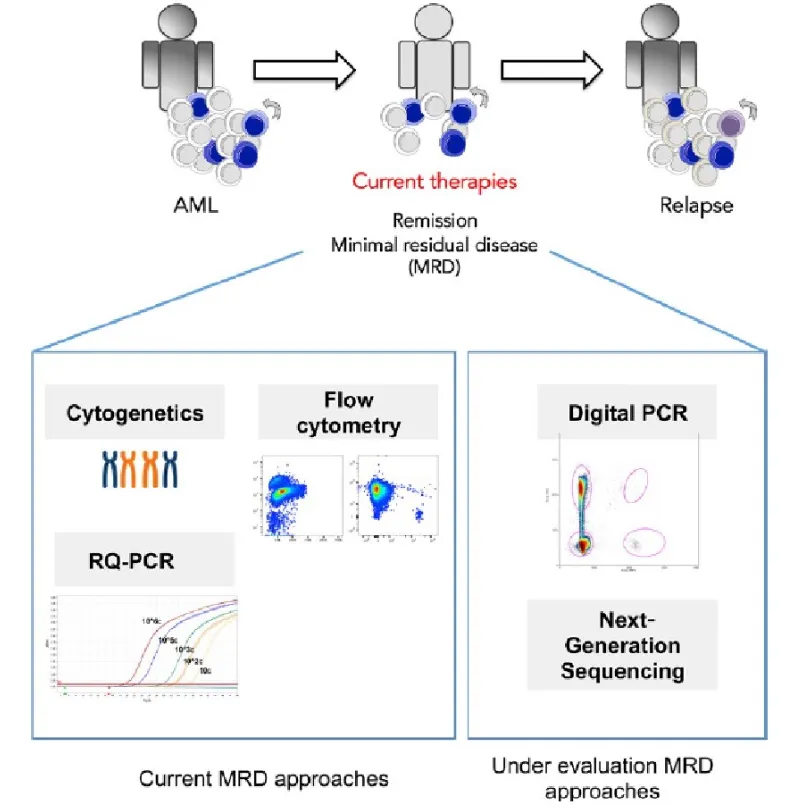
Beyond providing the reference standard itself, CB-Gene Bio offers end-to-end support to maximize your MRD assay performance:
Performance Verification: Validate the sensitivity, specificity, and precision of pan-tumor MRD ctDNA detection assays (compatible with both tumor-agnostic and tumor-informed platforms).
Method Optimization: Assist in refining new MRD detection workflows (e.g., library preparation, sequencing parameters) using the standard to ensure consistency.
Daily Quality Control (QC) Support: Guide routine QC protocols to monitor experimental stability—critical for long-term assay reliability.
Technical Consultation: Provide expert advice on interpreting results (e.g., dilution fold confirmation, AF% validation) and troubleshooting issues like low signal detection.
What sets Package-Ref™ apart from other MRD reference standards? Its unique design addresses the most pressing needs of MRD researchers and clinicians:
Ultra-Low Frequency Detection Capability
With a minimum AF% of 0.005%, the standard matches the sensitivity required for early-stage cancer MRD detection (e.g., BRAF , where ctDNA AF% can be as low as 0.047%). This ensures your assay can reliably detect residual tumor DNA before clinical recurrence.
Pan-Tumor Compatibility
Covering 45 mutation sites across 9+ key oncogenes (including BRAF p.V600E, PIK3CA p.H1047R, and TP53 c.783-2A>C), the standard supports MRD detection for multiple cancer types (e.g., colorectal, breast, lung, ovarian cancer). No need to purchase separate standards for different tumors—reducing cost and complexity.
Dual Quality Control Validation
Every batch is verified via both ddPCR (for precise AF% quantification) and NGS (for broad mutation site coverage). This dual QC ensures the standard’s accuracy, eliminating false positives/negatives in your assays.
Sample-Mimicking Design
Ultrasonicated ctDNA closely replicates the size and structure of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) in clinical plasma samples. This mimics real-world testing conditions, making validation results more relevant to clinical practice.
Long-Term Stability
With a 36-month shelf life at -25℃ ~ -15℃, the standard avoids frequent reordering and ensures consistent performance across months of experiments—ideal for long-term IVD development projects.
Our streamlined process ensures you get the right support, fast—from initial inquiry to post-purchase success:
Start with a 1:1 consultation to understand your specific needs (e.g., target cancer types, assay platform—tumor-agnostic vs. tumor-informed, required AF% ranges). Our team reviews your workflow to recommend the optimal usage of the Package-Ref™ standard (e.g., dilution protocols for ultra-low AF% testing).
Once ordered, the standard is shipped with insulated packaging to maintain -25℃ ~ -15℃ conditions, ensuring no degradation during transit. We include a detailed user manual with step-by-step instructions: thawing guidelines, dilution fold confirmation (e.g., validating 0.5% → 0.05% → 0.005% AF%), and QC assay setup (ddPCR/NGS).
Provide real-time technical support (via email or call) to assist with assay setup and result interpretation. For example, if you need to confirm BRAF p.V600E AF% in the 0.005% standard, our team can share optimized ddPCR protocols. We also offer validation check-ins to ensure the standard integrates seamlessly with your workflow (e.g., verifying that your assay consistently detects 0.005% AF% across 10+ replicates).
Conduct follow-up checks to address any long-term issues (e.g., storage-related stability concerns). We also share updates on new mutation site additions or protocol optimizations to keep your MRD assays aligned with the latest clinical guidelines.
Package-Ref™ MRD Cocktail Reference Standard is more than a product—it’s a partner in ensuring reliable, clinically relevant MRD results. Whether you’re developing a new IVD assay, optimizing an LDT workflow, or monitoring daily QC, our highly characterized standard and expert support will help you achieve consistent, accurate performance.
Contact CB-Gene Bio today to learn more about ordering, custom configurations (e.g., additional mutation sites), or technical consultations.
Name | Package-Ref™ MRD Cocktail Reference Standard |
Cat. No. | CBP90040 |
Format | ctDNA (ultrasonic treatment) |
Size | 0.5ug/vial * 4 vial |
Mutation site | 45 Mutation sites |
AF% | 0%、0.005%、0.05%、0.5% |
Quality Control Methods | ddPCR、NGS |
Inventory Status | In Stock |
Buffer | Tris-EDTA |
Storage Conditions | -25℃~ -15℃ |
Expiry | 36 months from the date of manufacture |
MRD Detection Technology
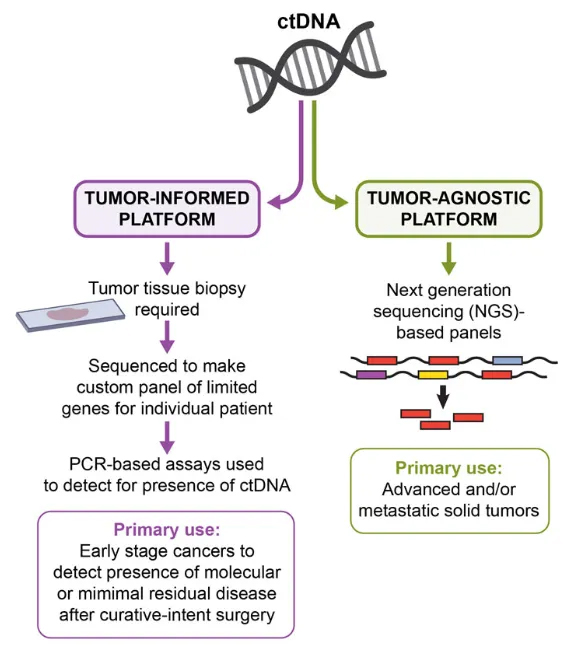
There are two main technical routes for MRD detection of ctDNA: tumor-agnostic assays and tumor-informed assays. Tumor-agnostic assays only detect plasma and use fixed panels (generally driver genes and targeted drug genes, and multi-omics methods) and analytical methods to detect and analyze ctDNA.
Tumor-informed assays require sequencing of primary tumor tissue (usually WES) to identify the patient's specific genomic variation profile, and then customize a personalized panel to test ctDNA, which means that both tissue and plasma need to be tested.
One of the most difficult aspects of MRD technology is the ability and stability to detect ultra-low frequency mutations. Taking non-small cell lung cancer as an example, the median cfDNA concentration in the plasma of early NSCLC patients is 7.69 ng/mL, which is equivalent to about 20,000 haploid genomes (3.3pg) in 10 mL of plasma (20ml of whole blood). Considering the loss of cfDNA during library construction and the presence of at least two identical variant gene sequences, the limit molecular signal detected by ctDNA in 10 mL of plasma is 0.02%. In addition, according to the TRACERx research data, in the case of a tumor volume of 1 cm3, 10 mL of plasma contains about 2 tumor-derived DNA molecules. Therefore, when performing MRD detection in NSCLC, the detection method must be able to stably detect ctDNA with an abundance of ≥ 0.02%. There is an important technical strategy here, which is the Sample Level strategy. For Site level of 0.02% or even lower, the sensitivity can be improved through Samples Level.
Detailed Data
The development of MRD diagnostic IVD for ctDNA detection requires performance evaluation, and naturally the development of standard products. Kebai Gene is a research and development and production company focusing on diagnostic positive reference products, detection limit reference products, and precision reference products in IVD research and development. For the development of ultra-low frequency standards for ctDNA, we launched our MRD standard: Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard.
Cat.No. | Name | %AF | Specification | Concentration | Remarks |
CBP90040-1 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0.5% | 0.50% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | Optimized ddPCR assay |
CBP90040-2 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0.05% | 0.05% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | Dilution fold-confirmation |
CBP90040-3 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0.005% | 0.005% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | Dilution fold-confirmation |
CBP90040-4 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0% | 0.00% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | ddPCR assay |
Dilution Multiple Verification Data
GENE | Mutation | AF% of MRD-0.5% ctDNA | AF% of MRD-0.05% ctDNA | AF% of MRD-0.005% ctDNA |
BRAF | p.V600E | 5.33 | 0.54 | 0.047 |
ACVR2A | p.K437Rfs*5 | 3.98 | 0.40 | 0.038 |
PIK3CA | p.H1047R | 2.81 | 0.26 | N/A |
BRCA1 | p.D435Y | 2.53 | 0.24 | N/A |
BRCA2 | p.N1784Tfs*7 | 2.35 | 0.23 | N/A |
BRCA2 | p.E2292A | 1.35 | 0.14 | N/A |
TP53 | c.783-2A>C | 1.02 | 0.11 | N/A |
CDKN2A | p.R80* | 0.92 | 0.10 | N/A |
HLA-A | p.R45Afs*32 | 1.25 | 0.11 | N/A |
This is a multi-gene, multi-site panel standard with a wide range of gene and site coverage and rich mutation types. It is very suitable as a reference and quality control product for LDT and IVD testing.
Product application
1.Performance verification for pan-tumor MRD ctDNA detection
2.For routine quality control of pan-tumor MRD ctDNA detection
Package-Ref™ MRD Cocktail Reference Standard is a specialized ctDNA-based reference material tailored for pan-tumor MRD detection quality control. MRD—defined as residual tumor cells or molecular markers remaining post-treatment—requires ultra-sensitive detection to predict recurrence and guide clinical decisions. This product addresses the core pain point of ultra-low frequency mutation detection, with a minimum detectable mutation frequency of 0.005% (5 mutant molecules per 100,000 total molecules), enabling validation of even the most sensitive MRD assays.
Crafted from ultrasonicated ctDNA (to mimic real-world clinical samples), the standard is supplied in a ready-to-use format, eliminating the need for complex preprocessing and ensuring consistency across experiments.

Beyond providing the reference standard itself, CB-Gene Bio offers end-to-end support to maximize your MRD assay performance:
Performance Verification: Validate the sensitivity, specificity, and precision of pan-tumor MRD ctDNA detection assays (compatible with both tumor-agnostic and tumor-informed platforms).
Method Optimization: Assist in refining new MRD detection workflows (e.g., library preparation, sequencing parameters) using the standard to ensure consistency.
Daily Quality Control (QC) Support: Guide routine QC protocols to monitor experimental stability—critical for long-term assay reliability.
Technical Consultation: Provide expert advice on interpreting results (e.g., dilution fold confirmation, AF% validation) and troubleshooting issues like low signal detection.
What sets Package-Ref™ apart from other MRD reference standards? Its unique design addresses the most pressing needs of MRD researchers and clinicians:
Ultra-Low Frequency Detection Capability
With a minimum AF% of 0.005%, the standard matches the sensitivity required for early-stage cancer MRD detection (e.g., BRAF , where ctDNA AF% can be as low as 0.047%). This ensures your assay can reliably detect residual tumor DNA before clinical recurrence.
Pan-Tumor Compatibility
Covering 45 mutation sites across 9+ key oncogenes (including BRAF p.V600E, PIK3CA p.H1047R, and TP53 c.783-2A>C), the standard supports MRD detection for multiple cancer types (e.g., colorectal, breast, lung, ovarian cancer). No need to purchase separate standards for different tumors—reducing cost and complexity.
Dual Quality Control Validation
Every batch is verified via both ddPCR (for precise AF% quantification) and NGS (for broad mutation site coverage). This dual QC ensures the standard’s accuracy, eliminating false positives/negatives in your assays.
Sample-Mimicking Design
Ultrasonicated ctDNA closely replicates the size and structure of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) in clinical plasma samples. This mimics real-world testing conditions, making validation results more relevant to clinical practice.
Long-Term Stability
With a 36-month shelf life at -25℃ ~ -15℃, the standard avoids frequent reordering and ensures consistent performance across months of experiments—ideal for long-term IVD development projects.
Our streamlined process ensures you get the right support, fast—from initial inquiry to post-purchase success:
Start with a 1:1 consultation to understand your specific needs (e.g., target cancer types, assay platform—tumor-agnostic vs. tumor-informed, required AF% ranges). Our team reviews your workflow to recommend the optimal usage of the Package-Ref™ standard (e.g., dilution protocols for ultra-low AF% testing).
Once ordered, the standard is shipped with insulated packaging to maintain -25℃ ~ -15℃ conditions, ensuring no degradation during transit. We include a detailed user manual with step-by-step instructions: thawing guidelines, dilution fold confirmation (e.g., validating 0.5% → 0.05% → 0.005% AF%), and QC assay setup (ddPCR/NGS).
Provide real-time technical support (via email or call) to assist with assay setup and result interpretation. For example, if you need to confirm BRAF p.V600E AF% in the 0.005% standard, our team can share optimized ddPCR protocols. We also offer validation check-ins to ensure the standard integrates seamlessly with your workflow (e.g., verifying that your assay consistently detects 0.005% AF% across 10+ replicates).
Conduct follow-up checks to address any long-term issues (e.g., storage-related stability concerns). We also share updates on new mutation site additions or protocol optimizations to keep your MRD assays aligned with the latest clinical guidelines.
Package-Ref™ MRD Cocktail Reference Standard is more than a product—it’s a partner in ensuring reliable, clinically relevant MRD results. Whether you’re developing a new IVD assay, optimizing an LDT workflow, or monitoring daily QC, our highly characterized standard and expert support will help you achieve consistent, accurate performance.
Contact CB-Gene Bio today to learn more about ordering, custom configurations (e.g., additional mutation sites), or technical consultations.
Name | Package-Ref™ MRD Cocktail Reference Standard |
Cat. No. | CBP90040 |
Format | ctDNA (ultrasonic treatment) |
Size | 0.5ug/vial * 4 vial |
Mutation site | 45 Mutation sites |
AF% | 0%、0.005%、0.05%、0.5% |
Quality Control Methods | ddPCR、NGS |
Inventory Status | In Stock |
Buffer | Tris-EDTA |
Storage Conditions | -25℃~ -15℃ |
Expiry | 36 months from the date of manufacture |
MRD Detection Technology
There are two main technical routes for MRD detection of ctDNA: tumor-agnostic assays and tumor-informed assays. Tumor-agnostic assays only detect plasma and use fixed panels (generally driver genes and targeted drug genes, and multi-omics methods) and analytical methods to detect and analyze ctDNA.
Tumor-informed assays require sequencing of primary tumor tissue (usually WES) to identify the patient's specific genomic variation profile, and then customize a personalized panel to test ctDNA, which means that both tissue and plasma need to be tested.
One of the most difficult aspects of MRD technology is the ability and stability to detect ultra-low frequency mutations. Taking non-small cell lung cancer as an example, the median cfDNA concentration in the plasma of early NSCLC patients is 7.69 ng/mL, which is equivalent to about 20,000 haploid genomes (3.3pg) in 10 mL of plasma (20ml of whole blood). Considering the loss of cfDNA during library construction and the presence of at least two identical variant gene sequences, the limit molecular signal detected by ctDNA in 10 mL of plasma is 0.02%. In addition, according to the TRACERx research data, in the case of a tumor volume of 1 cm3, 10 mL of plasma contains about 2 tumor-derived DNA molecules. Therefore, when performing MRD detection in NSCLC, the detection method must be able to stably detect ctDNA with an abundance of ≥ 0.02%. There is an important technical strategy here, which is the Sample Level strategy. For Site level of 0.02% or even lower, the sensitivity can be improved through Samples Level.

Detailed Data
The development of MRD diagnostic IVD for ctDNA detection requires performance evaluation, and naturally the development of standard products. Kebai Gene is a research and development and production company focusing on diagnostic positive reference products, detection limit reference products, and precision reference products in IVD research and development. For the development of ultra-low frequency standards for ctDNA, we launched our MRD standard: Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard.
Cat.No. | Name | %AF | Specification | Concentration | Remarks |
CBP90040-1 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0.5% | 0.50% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | Optimized ddPCR assay |
CBP90040-2 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0.05% | 0.05% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | Dilution fold-confirmation |
CBP90040-3 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0.005% | 0.005% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | Dilution fold-confirmation |
CBP90040-4 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0% | 0.00% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | ddPCR assay |
Dilution Multiple Verification Data
GENE | Mutation | AF% of MRD-0.5% ctDNA | AF% of MRD-0.05% ctDNA | AF% of MRD-0.005% ctDNA |
BRAF | p.V600E | 5.33 | 0.54 | 0.047 |
ACVR2A | p.K437Rfs*5 | 3.98 | 0.40 | 0.038 |
PIK3CA | p.H1047R | 2.81 | 0.26 | N/A |
BRCA1 | p.D435Y | 2.53 | 0.24 | N/A |
BRCA2 | p.N1784Tfs*7 | 2.35 | 0.23 | N/A |
BRCA2 | p.E2292A | 1.35 | 0.14 | N/A |
TP53 | c.783-2A>C | 1.02 | 0.11 | N/A |
CDKN2A | p.R80* | 0.92 | 0.10 | N/A |
HLA-A | p.R45Afs*32 | 1.25 | 0.11 | N/A |
This is a multi-gene, multi-site panel standard with a wide range of gene and site coverage and rich mutation types. It is very suitable as a reference and quality control product for LDT and IVD testing.
Product application
1.Performance verification for pan-tumor MRD ctDNA detection
2.For routine quality control of pan-tumor MRD ctDNA detection
MRD Detection Technology
There are two main technical routes for MRD detection of ctDNA: tumor-agnostic assays and tumor-informed assays. Tumor-agnostic assays only detect plasma and use fixed panels (generally driver genes and targeted drug genes, and multi-omics methods) and analytical methods to detect and analyze ctDNA.
Tumor-informed assays require sequencing of primary tumor tissue (usually WES) to identify the patient's specific genomic variation profile, and then customize a personalized panel to test ctDNA, which means that both tissue and plasma need to be tested.
One of the most difficult aspects of MRD technology is the ability and stability to detect ultra-low frequency mutations. Taking non-small cell lung cancer as an example, the median cfDNA concentration in the plasma of early NSCLC patients is 7.69 ng/mL, which is equivalent to about 20,000 haploid genomes (3.3pg) in 10 mL of plasma (20ml of whole blood). Considering the loss of cfDNA during library construction and the presence of at least two identical variant gene sequences, the limit molecular signal detected by ctDNA in 10 mL of plasma is 0.02%. In addition, according to the TRACERx research data, in the case of a tumor volume of 1 cm3, 10 mL of plasma contains about 2 tumor-derived DNA molecules. Therefore, when performing MRD detection in NSCLC, the detection method must be able to stably detect ctDNA with an abundance of ≥ 0.02%. There is an important technical strategy here, which is the Sample Level strategy. For Site level of 0.02% or even lower, the sensitivity can be improved through Samples Level.

MRD Detection Technology
There are two main technical routes for MRD detection of ctDNA: tumor-agnostic assays and tumor-informed assays. Tumor-agnostic assays only detect plasma and use fixed panels (generally driver genes and targeted drug genes, and multi-omics methods) and analytical methods to detect and analyze ctDNA.
Tumor-informed assays require sequencing of primary tumor tissue (usually WES) to identify the patient's specific genomic variation profile, and then customize a personalized panel to test ctDNA, which means that both tissue and plasma need to be tested.
One of the most difficult aspects of MRD technology is the ability and stability to detect ultra-low frequency mutations. Taking non-small cell lung cancer as an example, the median cfDNA concentration in the plasma of early NSCLC patients is 7.69 ng/mL, which is equivalent to about 20,000 haploid genomes (3.3pg) in 10 mL of plasma (20ml of whole blood). Considering the loss of cfDNA during library construction and the presence of at least two identical variant gene sequences, the limit molecular signal detected by ctDNA in 10 mL of plasma is 0.02%. In addition, according to the TRACERx research data, in the case of a tumor volume of 1 cm3, 10 mL of plasma contains about 2 tumor-derived DNA molecules. Therefore, when performing MRD detection in NSCLC, the detection method must be able to stably detect ctDNA with an abundance of ≥ 0.02%. There is an important technical strategy here, which is the Sample Level strategy. For Site level of 0.02% or even lower, the sensitivity can be improved through Samples Level.

Detailed Data
The development of MRD diagnostic IVD for ctDNA detection requires performance evaluation, and naturally the development of standard products. Kebai Gene is a research and development and production company focusing on diagnostic positive reference products, detection limit reference products, and precision reference products in IVD research and development. For the development of ultra-low frequency standards for ctDNA, we launched our MRD standard: Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard.
Cat.No. | Name | %AF | Specification | Concentration | Remarks |
CBP90040-1 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0.5% | 0.50% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | Optimized ddPCR assay |
CBP90040-2 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0.05% | 0.05% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | Dilution fold-confirmation |
CBP90040-3 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0.005% | 0.005% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | Dilution fold-confirmation |
CBP90040-4 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0% | 0.00% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | ddPCR assay |
Detailed Data
The development of MRD diagnostic IVD for ctDNA detection requires performance evaluation, and naturally the development of standard products. Kebai Gene is a research and development and production company focusing on diagnostic positive reference products, detection limit reference products, and precision reference products in IVD research and development. For the development of ultra-low frequency standards for ctDNA, we launched our MRD standard: Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard.
Cat.No. | Name | %AF | Specification | Concentration | Remarks |
CBP90040-1 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0.5% | 0.50% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | Optimized ddPCR assay |
CBP90040-2 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0.05% | 0.05% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | Dilution fold-confirmation |
CBP90040-3 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0.005% | 0.005% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | Dilution fold-confirmation |
CBP90040-4 | Package-RefTM MRD Cocktail Reference Standard-0% | 0.00% | 500 ng/vial | 20 ng/µL | ddPCR assay |
Dilution Multiple Verification Data
GENE | Mutation | AF% of MRD-0.5% ctDNA | AF% of MRD-0.05% ctDNA | AF% of MRD-0.005% ctDNA |
BRAF | p.V600E | 5.33 | 0.54 | 0.047 |
ACVR2A | p.K437Rfs*5 | 3.98 | 0.40 | 0.038 |
PIK3CA | p.H1047R | 2.81 | 0.26 | N/A |
BRCA1 | p.D435Y | 2.53 | 0.24 | N/A |
BRCA2 | p.N1784Tfs*7 | 2.35 | 0.23 | N/A |
BRCA2 | p.E2292A | 1.35 | 0.14 | N/A |
TP53 | c.783-2A>C | 1.02 | 0.11 | N/A |
CDKN2A | p.R80* | 0.92 | 0.10 | N/A |
HLA-A | p.R45Afs*32 | 1.25 | 0.11 | N/A |
This is a multi-gene, multi-site panel standard with a wide range of gene and site coverage and rich mutation types. It is very suitable as a reference and quality control product for LDT and IVD testing.
Dilution Multiple Verification Data
GENE | Mutation | AF% of MRD-0.5% ctDNA | AF% of MRD-0.05% ctDNA | AF% of MRD-0.005% ctDNA |
BRAF | p.V600E | 5.33 | 0.54 | 0.047 |
ACVR2A | p.K437Rfs*5 | 3.98 | 0.40 | 0.038 |
PIK3CA | p.H1047R | 2.81 | 0.26 | N/A |
BRCA1 | p.D435Y | 2.53 | 0.24 | N/A |
BRCA2 | p.N1784Tfs*7 | 2.35 | 0.23 | N/A |
BRCA2 | p.E2292A | 1.35 | 0.14 | N/A |
TP53 | c.783-2A>C | 1.02 | 0.11 | N/A |
CDKN2A | p.R80* | 0.92 | 0.10 | N/A |
HLA-A | p.R45Afs*32 | 1.25 | 0.11 | N/A |
This is a multi-gene, multi-site panel standard with a wide range of gene and site coverage and rich mutation types. It is very suitable as a reference and quality control product for LDT and IVD testing.
Product Application
1.Performance verification for pan-tumor MRD ctDNA detection
2.For routine quality control of pan-tumor MRD ctDNA detection
Product Application
1.Performance verification for pan-tumor MRD ctDNA detection
2.For routine quality control of pan-tumor MRD ctDNA detection