- Home
- Products
- Services
- Resources
- About Us
- News
- Contact

loading
CBPJ000-1/2/9/10/14/16
CBPJ000-1/2/9/10/14/16
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
Product Description
NIPT standards include Common chromosomal aneuploidy standards, Rare chromosome aneuploidy standards,sex chromosome aneuploidy standards,microdeletion and microduplication standards,and maternal-infant chromosome abnormality standards;
CB-Gene has launched Common chromosomal aneuploidy standards, including Trisomy 21 Reference Standard,Trisomy 13 Reference Standard, Trisomy 18 Reference Standard,,which are highly accurate, stable, and effective, ensuring the accuracy of detection.
Key Features
Entire workflow quality control
Common chromosomal aneuploidy standards uses human cell as raw materials to simulate real clinical samples, and can quality control the entire NIPT process starting from the extraction step;
Highly simulated clinical samples
The process is complete and the plasma ctDNA format can be customized to highly simulate clinical samples.
Compatible with multiple NIPT assay platforms
Common chromosomal aneuploidy standards are suitable for a variety of NIPT tests and can be used to evaluate whether the concentration of fetal cell-free DNA determined by high-throughput sequencing methods is accurate.
Comprehensive coverage of variants
High coverage, covering common clinical chromosomal abnormalities, including: Common chromosomal aneuploidy: T21/T13/T18;
Rare chromosomal aneuploidy: T9/T15;
Sex chromosome aneuploidy: Klinefelter's.
common microdeletion and microduplication syndrome types:11q23.3del, DGS, AS,PWS etc
Flexible portfolio of fetal fraction levels
By controlling the incorporation of fragmented DNA to set the fetal ratio, the product uses NGS to check the location of chromosomal abnormalities and CNV size, and quantify the fetal concentration. The fetal DNA ratio can be customized based on the test results and the detection limit can be determined.
Detection Methods
Common methods for screening chromosomal abnormalities include G-banding, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), DNA microarray (CMA), NIPT, NIPT-Plus, CNV-seq, etc.
Chromosome karyotype analysis (G-banding) is generally used to detect the number and large structural abnormalities of chromosomes, and is the gold standard for detection. FISH can theoretically detect information at any position in the genome, but it requires corresponding probes. Currently, the commonly used clinical test kits are for chromosomes 13, 18, 21 and sex chromosomes. NIPT and NIPT- Plus are based on NGS methods. NIPT uses Z scores to determine whether the chromosomes are abnormal. Non-invasive prenatal testing for single-gene diseases is for single-gene genetic diseases. DNA microarray mainly detects microdeletions and microduplications of chromosomes, and uses log R ratio to determine whether they are abnormal.
Detection method | Detection range | Disadvantages |
Chromosome karyotype analysis (G banding) | Analyze abnormalities in chromosome structure, loss of large chromosome fragments, duplications and abnormal positions | Cannot detect small (<5M) genomic variations |
DNA microarray (CMA) | Abnormal chromosome number and structure | Can only detect known abnormal chromosome positions |
DNA microarray (CMA) | Chromosome copy number variation, as well as chromosome microdeletion, microduplication, uniparental disomy | Cannot detect gene level, mainly for some common chromosomal abnormalities |
Non-invasive single gene disease detection | Monogenic genetic disease | Highly targeted, for a single disease |
NIPT (NGS) | Abnormal chromosome number | Cannot detect chromosome microdeletion/microduplication NIPT-plus (NGS) |
NIPT-plus (NGS) | Chromosome copy number variation, as well as chromosome microdeletions and microduplications | Can only be used as a screening method, not as a diagnostic method, and cannot detect genetic levels |
CNV-Seq | Whole genome detection, high sensitivity, high precision | Data processing is complex, and sample processing standards are high |
Down syndrome screening | Can only detect trisomy 18, trisomy 21 and neural tube defects | Limited detection range, low detection rate, and a certain probability of false positives |
Table 1. Comparison of common chromosome detection methods
Detailed data
Product Information | CBPJ0001 | CBPJ0002 | CBPJ0009 | CBPJ0010 | CBPJ0014 | CBPJ0016 | |
Format | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | |
Mutation | Trisomy 21 | Trisomy 18 | Trisomy 21 | Trisomy 13 | Trisomy 9 | Trisomy 21 | |
Karyotype | 47,XY,+21 | 47,XX,+18 | 47,XY,+21 | 47,XY,+13 | 47,XY,+9 | 47,XY,+21 | |
Representative Data | chr1 | 0.42 | -1.66 | 0.492 | -4.34 | -3.51 | -1.54 |
chr2 | -4.72 | -9.18 | -5.13 | -8.61 | 7.50 | -1.51 | |
chr3 | -2.42 | -3.05 | -1.16 | -1.7 | -2.27 | -0.47 | |
chr4 | -3.66 | -4.61 | -3.43 | -4.53 | -3.05 | -1.17 | |
chr5 | -0.88 | -4.11 | -1.96 | -2.72 | -3.34 | -2.29 | |
chr6 | -2.37 | -5.63 | -0.25 | -4.69 | -4.39 | -0.05 | |
chr7 | -0.48 | -1.48 | 2.377 | -2.6 | -3.37 | -0.96 | |
chr8 | -6.73 | -6.61 | -5.12 | -4.61 | -4.36 | -3.18 | |
chr9 | 1.44 | -2.26 | -0.17 | -6.17 | 78.07 | -3.97 | |
chr10 | -4.42 | -8.36 | -4.98 | -5.11 | -5.77 | -3.97 | |
chr11 | -0.75 | -2.41 | -2.81 | -2.48 | -2.07 | -1.97 | |
chr12 | 0.96 | -0.06 | 0.371 | -2.22 | -2.29 | -0.39 | |
chr13 | -3.67 | -9.08 | -8.04 | 88.57 | -4.74 | -2.15 | |
chr14 | -1.50 | -3.89 | 0.333 | -4.55 | -4.38 | -1.20 | |
chr15 | -0.78 | -2.91 | -1.48 | -7.82 | -6.80 | -4.18 | |
chr16 | -1.53 | -0.05 | -0.53 | -0.42 | -0.60 | -1.14 | |
chr17 | 2.49 | 0.98 | 1.497 | 0.31 | -2.05 | 0.80 | |
chr18 | -5.51 | 82.19 | -4.72 | -5.53 | -6.21 | -3.30 | |
chr19 | 3.55 | 3.2 | 2.758 | 1.88 | 1.73 | 2.38 | |
chr20 | -2.70 | -2.74 | -2.76 | -2.76 | -3.37 | -3.36 | |
chr21 | 62.87 | -2.86 | 63.01 | -3.5 | -4.24 | 63.34 | |
chr22 | -0.23 | -0.19 | 0.063 | -1.5 | -2.37 | -2.48 | |
Data Graph | 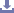 CBPJ0001 CBPJ0001 | ||||||
Intended Use | Research Use Only | ||||||
Unit Size | 1ug | ||||||
Concentration | Download for COA | ||||||
DNA electrophoresis | Download for COA | ||||||
Storage | 2-8℃ | ||||||
Expiry | 36 months from the date of manufacture | ||||||
Product Description
NIPT standards include Common chromosomal aneuploidy standards, Rare chromosome aneuploidy standards,sex chromosome aneuploidy standards,microdeletion and microduplication standards,and maternal-infant chromosome abnormality standards;
CB-Gene has launched Common chromosomal aneuploidy standards, including Trisomy 21 Reference Standard,Trisomy 13 Reference Standard, Trisomy 18 Reference Standard,,which are highly accurate, stable, and effective, ensuring the accuracy of detection.
Key Features
Entire workflow quality control
Common chromosomal aneuploidy standards uses human cell as raw materials to simulate real clinical samples, and can quality control the entire NIPT process starting from the extraction step;
Highly simulated clinical samples
The process is complete and the plasma ctDNA format can be customized to highly simulate clinical samples.
Compatible with multiple NIPT assay platforms
Common chromosomal aneuploidy standards are suitable for a variety of NIPT tests and can be used to evaluate whether the concentration of fetal cell-free DNA determined by high-throughput sequencing methods is accurate.
Comprehensive coverage of variants
High coverage, covering common clinical chromosomal abnormalities, including: Common chromosomal aneuploidy: T21/T13/T18;
Rare chromosomal aneuploidy: T9/T15;
Sex chromosome aneuploidy: Klinefelter's.
common microdeletion and microduplication syndrome types:11q23.3del, DGS, AS,PWS etc
Flexible portfolio of fetal fraction levels
By controlling the incorporation of fragmented DNA to set the fetal ratio, the product uses NGS to check the location of chromosomal abnormalities and CNV size, and quantify the fetal concentration. The fetal DNA ratio can be customized based on the test results and the detection limit can be determined.
Detection Methods
Common methods for screening chromosomal abnormalities include G-banding, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), DNA microarray (CMA), NIPT, NIPT-Plus, CNV-seq, etc.
Chromosome karyotype analysis (G-banding) is generally used to detect the number and large structural abnormalities of chromosomes, and is the gold standard for detection. FISH can theoretically detect information at any position in the genome, but it requires corresponding probes. Currently, the commonly used clinical test kits are for chromosomes 13, 18, 21 and sex chromosomes. NIPT and NIPT- Plus are based on NGS methods. NIPT uses Z scores to determine whether the chromosomes are abnormal. Non-invasive prenatal testing for single-gene diseases is for single-gene genetic diseases. DNA microarray mainly detects microdeletions and microduplications of chromosomes, and uses log R ratio to determine whether they are abnormal.
Detection method | Detection range | Disadvantages |
Chromosome karyotype analysis (G banding) | Analyze abnormalities in chromosome structure, loss of large chromosome fragments, duplications and abnormal positions | Cannot detect small (<5M) genomic variations |
DNA microarray (CMA) | Abnormal chromosome number and structure | Can only detect known abnormal chromosome positions |
DNA microarray (CMA) | Chromosome copy number variation, as well as chromosome microdeletion, microduplication, uniparental disomy | Cannot detect gene level, mainly for some common chromosomal abnormalities |
Non-invasive single gene disease detection | Monogenic genetic disease | Highly targeted, for a single disease |
NIPT (NGS) | Abnormal chromosome number | Cannot detect chromosome microdeletion/microduplication NIPT-plus (NGS) |
NIPT-plus (NGS) | Chromosome copy number variation, as well as chromosome microdeletions and microduplications | Can only be used as a screening method, not as a diagnostic method, and cannot detect genetic levels |
CNV-Seq | Whole genome detection, high sensitivity, high precision | Data processing is complex, and sample processing standards are high |
Down syndrome screening | Can only detect trisomy 18, trisomy 21 and neural tube defects | Limited detection range, low detection rate, and a certain probability of false positives |
Table 1. Comparison of common chromosome detection methods
Detailed data
Product Information | CBPJ0001 | CBPJ0002 | CBPJ0009 | CBPJ0010 | CBPJ0014 | CBPJ0016 | |
Format | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | |
Mutation | Trisomy 21 | Trisomy 18 | Trisomy 21 | Trisomy 13 | Trisomy 9 | Trisomy 21 | |
Karyotype | 47,XY,+21 | 47,XX,+18 | 47,XY,+21 | 47,XY,+13 | 47,XY,+9 | 47,XY,+21 | |
Representative Data | chr1 | 0.42 | -1.66 | 0.492 | -4.34 | -3.51 | -1.54 |
chr2 | -4.72 | -9.18 | -5.13 | -8.61 | 7.50 | -1.51 | |
chr3 | -2.42 | -3.05 | -1.16 | -1.7 | -2.27 | -0.47 | |
chr4 | -3.66 | -4.61 | -3.43 | -4.53 | -3.05 | -1.17 | |
chr5 | -0.88 | -4.11 | -1.96 | -2.72 | -3.34 | -2.29 | |
chr6 | -2.37 | -5.63 | -0.25 | -4.69 | -4.39 | -0.05 | |
chr7 | -0.48 | -1.48 | 2.377 | -2.6 | -3.37 | -0.96 | |
chr8 | -6.73 | -6.61 | -5.12 | -4.61 | -4.36 | -3.18 | |
chr9 | 1.44 | -2.26 | -0.17 | -6.17 | 78.07 | -3.97 | |
chr10 | -4.42 | -8.36 | -4.98 | -5.11 | -5.77 | -3.97 | |
chr11 | -0.75 | -2.41 | -2.81 | -2.48 | -2.07 | -1.97 | |
chr12 | 0.96 | -0.06 | 0.371 | -2.22 | -2.29 | -0.39 | |
chr13 | -3.67 | -9.08 | -8.04 | 88.57 | -4.74 | -2.15 | |
chr14 | -1.50 | -3.89 | 0.333 | -4.55 | -4.38 | -1.20 | |
chr15 | -0.78 | -2.91 | -1.48 | -7.82 | -6.80 | -4.18 | |
chr16 | -1.53 | -0.05 | -0.53 | -0.42 | -0.60 | -1.14 | |
chr17 | 2.49 | 0.98 | 1.497 | 0.31 | -2.05 | 0.80 | |
chr18 | -5.51 | 82.19 | -4.72 | -5.53 | -6.21 | -3.30 | |
chr19 | 3.55 | 3.2 | 2.758 | 1.88 | 1.73 | 2.38 | |
chr20 | -2.70 | -2.74 | -2.76 | -2.76 | -3.37 | -3.36 | |
chr21 | 62.87 | -2.86 | 63.01 | -3.5 | -4.24 | 63.34 | |
chr22 | -0.23 | -0.19 | 0.063 | -1.5 | -2.37 | -2.48 | |
Data Graph |  CBPJ0001 CBPJ0001 | ||||||
Intended Use | Research Use Only | ||||||
Unit Size | 1ug | ||||||
Concentration | Download for COA | ||||||
DNA electrophoresis | Download for COA | ||||||
Storage | 2-8℃ | ||||||
Expiry | 36 months from the date of manufacture | ||||||
Key Features
Entire workflow quality control
Common chromosomal aneuploidy standards uses human plasma as the matrix to simulate real clinical samples, and can quality control the entire NIPT process starting from the extraction step;
Highly simulated clinical samples
The process is complete and the plasma ctDNA format can be customized to highly simulate clinical samples.
Compatible with multiple NIPT assay platforms
Common chromosomal aneuploidy standards are suitable for a variety of NIPT tests and can be used to evaluate whether the concentration of fetal cell-free DNA determined by high-throughput sequencing methods is accurate.
Comprehensive coverage of variants
High coverage, covering common clinical chromosomal abnormalities, including: Common chromosomal aneuploidy: T21/T13/T18;
Rare chromosomal aneuploidy: T9/T15;
Sex chromosome aneuploidy: Klinefelter's.
common microdeletion and microduplication syndrome types:11q23.3del, DGS, AS,PWS etc
Flexible portfolio of fetal fraction levels
By controlling the incorporation of fragmented DNA to set the fetal ratio, the product uses NGS to check the location of chromosomal abnormalities and CNV size, and quantify the fetal concentration. The fetal DNA ratio can be customized based on the test results and the detection limit can be determined.
Key Features
Entire workflow quality control
Common chromosomal aneuploidy standards uses human plasma as the matrix to simulate real clinical samples, and can quality control the entire NIPT process starting from the extraction step;
Highly simulated clinical samples
The process is complete and the plasma ctDNA format can be customized to highly simulate clinical samples.
Compatible with multiple NIPT assay platforms
Common chromosomal aneuploidy standards are suitable for a variety of NIPT tests and can be used to evaluate whether the concentration of fetal cell-free DNA determined by high-throughput sequencing methods is accurate.
Comprehensive coverage of variants
High coverage, covering common clinical chromosomal abnormalities, including: Common chromosomal aneuploidy: T21/T13/T18;
Rare chromosomal aneuploidy: T9/T15;
Sex chromosome aneuploidy: Klinefelter's.
common microdeletion and microduplication syndrome types:11q23.3del, DGS, AS,PWS etc
Flexible portfolio of fetal fraction levels
By controlling the incorporation of fragmented DNA to set the fetal ratio, the product uses NGS to check the location of chromosomal abnormalities and CNV size, and quantify the fetal concentration. The fetal DNA ratio can be customized based on the test results and the detection limit can be determined.
Detection Methods
Common methods for screening chromosomal abnormalities include G-banding, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), DNA microarray (CMA), NIPT, NIPT-Plus, CNV-seq, etc.
Chromosome karyotype analysis (G-banding) is generally used to detect the number and large structural abnormalities of chromosomes, and is the gold standard for detection. FISH can theoretically detect information at any position in the genome, but it requires corresponding probes. Currently, the commonly used clinical test kits are for chromosomes 13, 18, 21 and sex chromosomes. NIPT and NIPT- Plus are based on NGS methods. NIPT uses Z scores to determine whether the chromosomes are abnormal. Non-invasive prenatal testing for single-gene diseases is for single-gene genetic diseases. DNA microarray mainly detects microdeletions and microduplications of chromosomes, and uses log R ratio to determine whether they are abnormal.
Detection method | Detection range | Disadvantages |
Chromosome karyotype analysis (G banding) | Analyze abnormalities in chromosome structure, loss of large chromosome fragments, duplications and abnormal positions | Cannot detect small (<5M) genomic variations |
DNA microarray (CMA) | Abnormal chromosome number and structure | Can only detect known abnormal chromosome positions |
DNA microarray (CMA) | Chromosome copy number variation, as well as chromosome microdeletion, microduplication, uniparental disomy | Cannot detect gene level, mainly for some common chromosomal abnormalities |
Non-invasive single gene disease detection | Monogenic genetic disease | Highly targeted, for a single disease |
NIPT (NGS) | Abnormal chromosome number | Cannot detect chromosome microdeletion/microduplication NIPT-plus (NGS) |
NIPT-plus (NGS) | Chromosome copy number variation, as well as chromosome microdeletions and microduplications | Can only be used as a screening method, not as a diagnostic method, and cannot detect genetic levels |
CNV-Seq | Whole genome detection, high sensitivity, high precision | Data processing is complex, and sample processing standards are high |
Down syndrome screening | Can only detect trisomy 18, trisomy 21 and neural tube defects | Limited detection range, low detection rate, and a certain probability of false positives |
Table 1. Comparison of common chromosome detection methods
Detection Methods
Common methods for screening chromosomal abnormalities include G-banding, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), DNA microarray (CMA), NIPT, NIPT-Plus, CNV-seq, etc.
Chromosome karyotype analysis (G-banding) is generally used to detect the number and large structural abnormalities of chromosomes, and is the gold standard for detection. FISH can theoretically detect information at any position in the genome, but it requires corresponding probes. Currently, the commonly used clinical test kits are for chromosomes 13, 18, 21 and sex chromosomes. NIPT and NIPT- Plus are based on NGS methods. NIPT uses Z scores to determine whether the chromosomes are abnormal. Non-invasive prenatal testing for single-gene diseases is for single-gene genetic diseases. DNA microarray mainly detects microdeletions and microduplications of chromosomes, and uses log R ratio to determine whether they are abnormal.
Detection method | Detection range | Disadvantages |
Chromosome karyotype analysis (G banding) | Analyze abnormalities in chromosome structure, loss of large chromosome fragments, duplications and abnormal positions | Cannot detect small (<5M) genomic variations |
DNA microarray (CMA) | Abnormal chromosome number and structure | Can only detect known abnormal chromosome positions |
DNA microarray (CMA) | Chromosome copy number variation, as well as chromosome microdeletion, microduplication, uniparental disomy | Cannot detect gene level, mainly for some common chromosomal abnormalities |
Non-invasive single gene disease detection | Monogenic genetic disease | Highly targeted, for a single disease |
NIPT (NGS) | Abnormal chromosome number | Cannot detect chromosome microdeletion/microduplication NIPT-plus (NGS) |
NIPT-plus (NGS) | Chromosome copy number variation, as well as chromosome microdeletions and microduplications | Can only be used as a screening method, not as a diagnostic method, and cannot detect genetic levels |
CNV-Seq | Whole genome detection, high sensitivity, high precision | Data processing is complex, and sample processing standards are high |
Down syndrome screening | Can only detect trisomy 18, trisomy 21 and neural tube defects | Limited detection range, low detection rate, and a certain probability of false positives |
Table 1. Comparison of common chromosome detection methods
Detailed data
Product Information | CBPJ0001 | CBPJ0002 | CBPJ0009 | CBPJ0010 | CBPJ0014 | CBPJ0016 | |
Format | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | |
Mutation | Trisomy 21 | Trisomy 18 | Trisomy 21 | Trisomy 13 | Trisomy 9 | Trisomy 21 | |
Karyotype | 47,XY,+21 | 47,XX,+18 | 47,XY,+21 | 47,XY,+13 | 47,XY,+9 | 47,XY,+21 | |
Representative Data | chr1 | 0.42 | -1.66 | 0.492 | -4.34 | -3.51 | -1.54 |
chr2 | -4.72 | -9.18 | -5.13 | -8.61 | 7.50 | -1.51 | |
chr3 | -2.42 | -3.05 | -1.16 | -1.7 | -2.27 | -0.47 | |
chr4 | -3.66 | -4.61 | -3.43 | -4.53 | -3.05 | -1.17 | |
chr5 | -0.88 | -4.11 | -1.96 | -2.72 | -3.34 | -2.29 | |
chr6 | -2.37 | -5.63 | -0.25 | -4.69 | -4.39 | -0.05 | |
chr7 | -0.48 | -1.48 | 2.377 | -2.6 | -3.37 | -0.96 | |
chr8 | -6.73 | -6.61 | -5.12 | -4.61 | -4.36 | -3.18 | |
chr9 | 1.44 | -2.26 | -0.17 | -6.17 | 78.07 | -3.97 | |
chr10 | -4.42 | -8.36 | -4.98 | -5.11 | -5.77 | -3.97 | |
chr11 | -0.75 | -2.41 | -2.81 | -2.48 | -2.07 | -1.97 | |
chr12 | 0.96 | -0.06 | 0.371 | -2.22 | -2.29 | -0.39 | |
chr13 | -3.67 | -9.08 | -8.04 | 88.57 | -4.74 | -2.15 | |
chr14 | -1.50 | -3.89 | 0.333 | -4.55 | -4.38 | -1.20 | |
chr15 | -0.78 | -2.91 | -1.48 | -7.82 | -6.80 | -4.18 | |
chr16 | -1.53 | -0.05 | -0.53 | -0.42 | -0.60 | -1.14 | |
chr17 | 2.49 | 0.98 | 1.497 | 0.31 | -2.05 | 0.80 | |
chr18 | -5.51 | 82.19 | -4.72 | -5.53 | -6.21 | -3.30 | |
chr19 | 3.55 | 3.2 | 2.758 | 1.88 | 1.73 | 2.38 | |
chr20 | -2.70 | -2.74 | -2.76 | -2.76 | -3.37 | -3.36 | |
chr21 | 62.87 | -2.86 | 63.01 | -3.5 | -4.24 | 63.34 | |
chr22 | -0.23 | -0.19 | 0.063 | -1.5 | -2.37 | -2.48 | |
Data Graph |  CBPJ0001 CBPJ0001 | ||||||
Intended Use | Research Use Only | ||||||
Unit Size | 1ug | ||||||
Concentration | Download for COA | ||||||
DNA electrophoresis | Download for COA | ||||||
Storage | 2-8℃ | ||||||
Expiry | 36 months from the date of manufacture | ||||||
Detailed data
Product Information | CBPJ0001 | CBPJ0002 | CBPJ0009 | CBPJ0010 | CBPJ0014 | CBPJ0016 | |
Format | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | Genomic DNA | |
Mutation | Trisomy 21 | Trisomy 18 | Trisomy 21 | Trisomy 13 | Trisomy 9 | Trisomy 21 | |
Karyotype | 47,XY,+21 | 47,XX,+18 | 47,XY,+21 | 47,XY,+13 | 47,XY,+9 | 47,XY,+21 | |
Representative Data | chr1 | 0.42 | -1.66 | 0.492 | -4.34 | -3.51 | -1.54 |
chr2 | -4.72 | -9.18 | -5.13 | -8.61 | 7.50 | -1.51 | |
chr3 | -2.42 | -3.05 | -1.16 | -1.7 | -2.27 | -0.47 | |
chr4 | -3.66 | -4.61 | -3.43 | -4.53 | -3.05 | -1.17 | |
chr5 | -0.88 | -4.11 | -1.96 | -2.72 | -3.34 | -2.29 | |
chr6 | -2.37 | -5.63 | -0.25 | -4.69 | -4.39 | -0.05 | |
chr7 | -0.48 | -1.48 | 2.377 | -2.6 | -3.37 | -0.96 | |
chr8 | -6.73 | -6.61 | -5.12 | -4.61 | -4.36 | -3.18 | |
chr9 | 1.44 | -2.26 | -0.17 | -6.17 | 78.07 | -3.97 | |
chr10 | -4.42 | -8.36 | -4.98 | -5.11 | -5.77 | -3.97 | |
chr11 | -0.75 | -2.41 | -2.81 | -2.48 | -2.07 | -1.97 | |
chr12 | 0.96 | -0.06 | 0.371 | -2.22 | -2.29 | -0.39 | |
chr13 | -3.67 | -9.08 | -8.04 | 88.57 | -4.74 | -2.15 | |
chr14 | -1.50 | -3.89 | 0.333 | -4.55 | -4.38 | -1.20 | |
chr15 | -0.78 | -2.91 | -1.48 | -7.82 | -6.80 | -4.18 | |
chr16 | -1.53 | -0.05 | -0.53 | -0.42 | -0.60 | -1.14 | |
chr17 | 2.49 | 0.98 | 1.497 | 0.31 | -2.05 | 0.80 | |
chr18 | -5.51 | 82.19 | -4.72 | -5.53 | -6.21 | -3.30 | |
chr19 | 3.55 | 3.2 | 2.758 | 1.88 | 1.73 | 2.38 | |
chr20 | -2.70 | -2.74 | -2.76 | -2.76 | -3.37 | -3.36 | |
chr21 | 62.87 | -2.86 | 63.01 | -3.5 | -4.24 | 63.34 | |
chr22 | -0.23 | -0.19 | 0.063 | -1.5 | -2.37 | -2.48 | |
Data Graph |  CBPJ0001 CBPJ0001 | ||||||
Intended Use | Research Use Only | ||||||
Unit Size | 1ug | ||||||
Concentration | Download for COA | ||||||
DNA electrophoresis | Download for COA | ||||||
Storage | 2-8℃ | ||||||
Expiry | 36 months from the date of manufacture | ||||||